Page 56 - Haematologica Atlas of Hematologic Cytology
P. 56
AB
CD
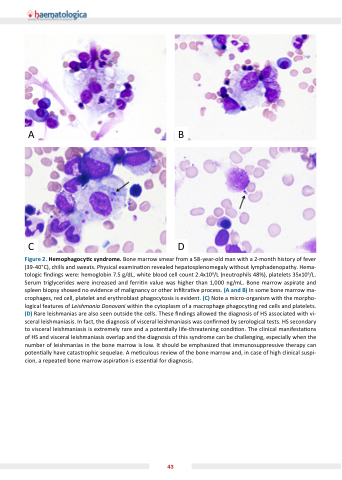
Figure 2. Hemophagocy c syndrome. Bone marrow smear from a 58-year-old man with a 2-month history of fever (39-40 C), chills and sweats. Physical examina on revealed hepatosplenomegaly without lymphadenopathy. Hema- tologic ndings were: hemoglobin 7.5 g/dL, white blood cell count 2.4x109/L (neutrophils 48%), platelets 35x109/L. Serum triglycerides were increased and ferri n value was higher than 1,000 ng/mL. Bone marrow aspirate and spleen biopsy showed no evidence of malignancy or other in ltra ve process. (A and B) In some bone marrow ma- crophages, red cell, platelet and erythroblast phagocytosis is evident. (C) Note a micro-organism with the morpho- logical features of Leishmania Donovani within the cytoplasm of a macrophage phagocy ng red cells and platelets. (D) Rare leishmanias are also seen outside the cells. These ndings allowed the diagnosis of HS associated with vi- sceral leishmaniasis. In fact, the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis was con rmed by serological tests. HS secondary to visceral leishmaniasis is extremely rare and a poten ally life-threatening condi on. The clinical manifesta ons of HS and visceral leishmaniasis overlap and the diagnosis of this syndrome can be challenging, especially when the number of leishmanias in the bone marrow is low. It should be emphasized that immunosuppressive therapy can poten ally have catastrophic sequelae. A me culous review of the bone marrow and, in case of high clinical suspi- cion, a repeated bone marrow aspira on is essen al for diagnosis.
43