Page 265 - Haematologica Atlas of Hematologic Cytology
P. 265
CHAPTER 32 - Immune thrombocytopenia
AB
CD
EF
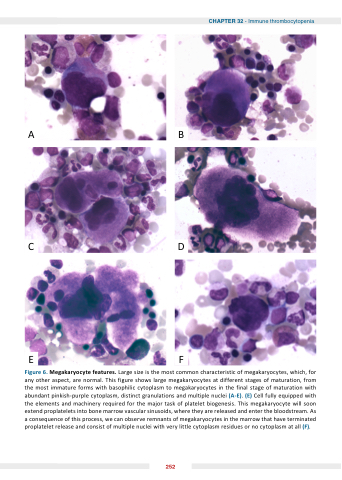
Figure 6 Megakaryocyte features Large size is is the most common characteristic of megakaryocytes which for any other aspect are normal This figure shows large megakaryocytes at at at different stages of maturation from the the most immature forms with with basophilic cytoplasm to to megakaryocytes in in the the final stage of maturation with with abundant pinkish-purple cytoplasm distinct granulations and multiple nuclei (A-E) (E) Cell fully equipped with the the elements and machinery required for the the major task of platelet biogenesis This megakaryocyte will soon extend proplatelets into bone marrow vascular sinusoids where they are released and enter the the bloodstream As a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
consequence of of this process we can observe remnants of of megakaryocytes in in the marrow that have terminated proplatelet release and consist of multiple nuclei with very little cytoplasm cytoplasm residues or no cytoplasm cytoplasm at at all (F) 252