Page 177 - Haematologica Atlas of Hematologic Cytology
P. 177
CHAPTER 18 - - - Mature T- and NK-cell neoplasms
AB
CD
EF
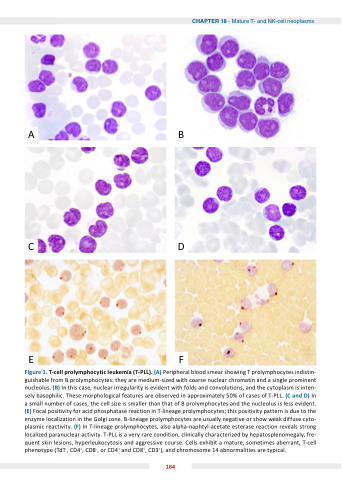
Figure 1 T T T cell prolymphocytic leu emia (T PLL) (A) Peripheral blood smear showing T T T prolymphocytes indistin- guishable from B prolymphocytes: they are medium-sized with coarse nuclear chromatin and a a a a a a a single prominent nucleolus ( ) In this case nuclear irregularity is is is evident with folds and and convolutions and and the cytoplasm is is is inten- sely basophilic These morphological features are observed in approximately 50% of of cases of of T-PLL (C and D) In a a a a a a a small small number of of cases the the cell size is is smaller than that of of B prolymphocytes and the the nucleolus is is less evident (E) Focal positivity positivity for acid phosphatase reaction in in T-lineage prolymphocytes this positivity positivity pattern is is due to the enzyme localization in in the Golgi zone B-lineage prolymphocytes are usually negative or show weak diffuse cyto- plasmic reactivity (F) In T-lineage prolymphocytes also alpha-naphtyl-acetate esterase reaction reveals strong localized paranuclear activity T-PLL is a a a a a a a a a a a a very rare condition clinically characterized by hepatosplenomegaly fre- quent skin lesions hyperleukocytosis and aggressive course Cells exhibit a a a a a a mature sometimes aberrant T-cell phenotype (TdT- CD4+ CD4+ CD8- or or CD4+ CD4+ and and CD8+ CD3+) and and chromosome 14 abnormalities are typical 164