Page 146 - Haematologica Atlas of Hematologic Cytology
P. 146
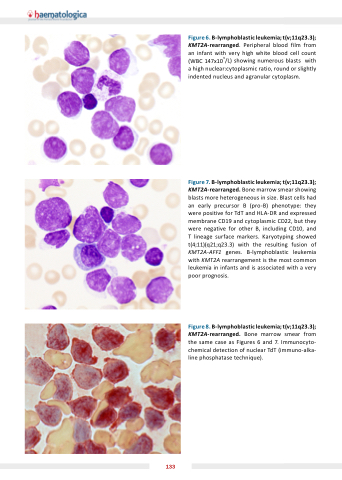
Figure lymphoblastic leu emia t(v 11 ) KMT2A rearranged Peripheral blood film from an an infant with very high white blood cell count (WBC 147x109/L) showing numerous blasts with with a a a a high nuclear:cytoplasmic ratio round or slightly indented nucleus and agranular cytoplasm Figure lymphoblastic leu emia t(v 11 ) KMT2A rearranged Bone marrow smear showing blasts more heterogeneous in size Blast cells had an early precursor B B (pro-B) phenotype: they were positive for TdT and and HLA-DR and and expressed membrane CD19 and cytoplasmic CD22 but they were negative for other B including CD10 and T lineage surface markers Karyotyping showed t(4 11)(q21 q23 3) with the resulting fusion of KMT2A-AFF1 genes B-lymphoblastic leukemia with KMT2A rearrangement is the most common leukemia in in infants and is associated with a a a a a a very poor prognosis Figure lymphoblastic leu emia t(v 11 ) KMT2A rearranged Bone marrow smear from the same case as as Figures 6 and 7 Immunocyto- chemical detection of nuclear TdT (immuno-alka- line phosphatase technique) 133