Page 132 - Haematologica Atlas of Hematologic Cytology
P. 132
AB
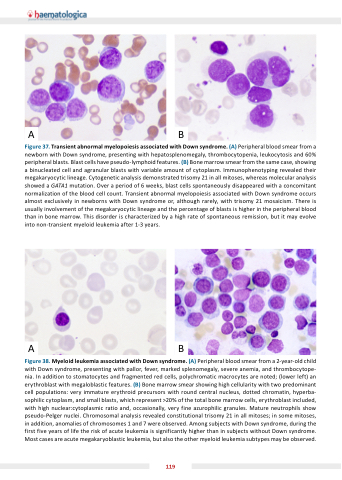
Figure . Transient abnormal myelopoiesis associated with Down syndrome. (A) Peripheral blood smear from a newborn with Down syndrome, presenting with hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis and 60% peripheral blasts. Blast cells have pseudo-lymphoid features. (B) Bone marrow smear from the same case, showing a binucleated cell and agranular blasts with variable amount of cytoplasm. Immunophenotyping revealed their megakaryocytic lineage. Cytogenetic analysis demonstrated trisomy 21 in all mitoses, whereas molecular analysis showed a GATA1 mutation. Over a period of 6 weeks, blast cells spontaneously disappeared with a concomitant normalization of the blood cell count. Transient abnormal myelopoiesis associated with Down syndrome occurs almost exclusively in newborns with Down syndrome or, although rarely, with trisomy 21 mosaicism. There is usually involvement of the megakaryocytic lineage and the percentage of blasts is higher in the peripheral blood than in bone marrow. This disorder is characterized by a high rate of spontaneous remission, but it may evolve into non-transient myeloid leukemia after 1-3 years.
AB
Figure . Myeloid leu emia associated with Down syndrome. (A) Peripheral blood smear from a 2-year-old child with Down syndrome, presenting with pallor, fever, marked splenomegaly, severe anemia, and thrombocytope- nia. In addition to stomatocytes and fragmented red cells, polychromatic macrocytes are noted; (lower left) an erythroblast with megaloblastic features. (B) Bone marrow smear showing high cellularity with two predominant cell populations: very immature erythroid precursors with round central nucleus, dotted chromatin, hyperba- sophilic cytoplasm, and small blasts, which represent >20% of the total bone marrow cells, erythroblast included, with high nuclear:cytoplasmic ratio and, occasionally, very fine azurophilic granules. Mature neutrophils show pseudo-Pelger nuclei. Chromosomal analysis revealed constitutional trisomy 21 in all mitoses; in some mitoses, in addition, anomalies of chromosomes 1 and 7 were observed. Among sub ects with Down syndrome, during the first five years of life the risk of acute leukemia is significantly higher than in subjects without Down syndrome. Most cases are acute megakaryoblastic leukemia, but also the other myeloid leukemia subtypes may be observed.
119