Page 131 - Haematologica Atlas of Hematologic Cytology
P. 131
CHAPTER 13 - Acute myeloid leukemia and related precursor neoplasms
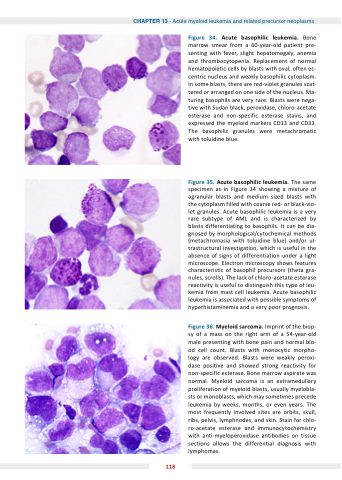
Figure 4 Acute basophilic leukemia Bone marrow smear from a a a a a 60-year-old patient pre- senting with fever slight hepatomegaly anemia and thrombocytopenia Replacement of normal hematopoietic cells by blasts with oval often ec- centric nucleus and weakly basophilic cytoplasm In some blasts there are red-violet granules scat- tered or arranged on on one side of the nucleus Ma- turing basophils are are very rare Blasts were nega- tive with Sudan black peroxidase chloro-acetate esterase esterase and and non-specific esterase esterase stains and and expressed the myeloid markers CD13 and CD33 The basophilic granules were metachromatic with toluidine blue Figure Figure Acute basophilic leukemia The same specimen as as as as in in Figure Figure 34 showing a a a a a a a a a a a mixture of agranular blasts blasts and medium sized blasts blasts with with the cytoplasm filled with with coarse red- or black-vio- let granules Acute basophilic leukemia is is a a a a a a a a a a a very rare subtype of AML and is is characterized by blasts differentiating to to basophils It can be dia- gnosed by morphological/cytochemical methods (metachromasia with toluidine blue) and/or ul-
trastructural investigation which is useful in in in the absence of of signs of of differentiation under a a a a a a a light microscope Electron microscopy shows features characteristic of of basophil precursors (theta gra- nules scrolls) The lack of of of chloro-acetate esterase reactivity is is is is useful to distinguish this type of of leu- kemia kemia kemia from mast cell leukemia leukemia Acute basophilic leukemia leukemia is is is associated with possible symptoms of hyperhistaminemia and a a a a a a a very poor prognosis Figure Myeloid sarcoma Imprint of the biop- sy of of a a a a a mass on the right arm of of a a a a a 54-year-old male presenting with bone pain and normal blo- od cell count Blasts with monocytic morpho- logy are observed Blasts were weakly peroxi- dase positive and showed strong reactivity for non-specific esterase Bone marrow aspirate was normal Myeloid sarcoma is an extramedullary proliferation of myeloid blasts usually myelobla- sts sts or monoblasts which may sometimes precede leukemia by weeks months or even years The most frequently involved sites are orbits skull ribs pelvis lymphnodes and skin Stain for chlo- ro-acetate esterase and immunocytochemistry with anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies on tissue sections allows the differential diagnosis with lymphomas 118