Page 85 - 2019_03-Haematologica-web
P. 85
NRF2 and Ara-C resistance in MDS
MLLPTD/WT /RUNX1-S291fs cells (Online Supplementary Figure S5A-D).We also performed immunohistochemistry assay to detect DUSP1 expression in 11 controls and 26 MDS patients (Figure 4B). NRF2 and DUSP1 IHC scores were both significantly increased in the higher-risk MDS group (high-risk and very high-risk by IPSS-R) compared to the control group (P<0.05) (Figure 4C). To better detect the small differences at the protein levels, we further com- pared the levels of NRF2 and DUSP1 with the BM mononuclear cells from Ara-C sensitive and Ara-C-resis- tant MDS patients by immunoblotting (Figure 4D). Samples from MDS patients who were responsive to Ara- C treatment were selected as Ara-C-sensitive MDS sam- ples. MDS patients in whom Ara-C treatment was seen to be ineffective were chosen as Ara-C-resistant cases. Elevated levels of NRF2 and DUSP1 were seen in the BM samples of Ara-C-resistant MDS patients by immunoblot-
ting analysis; this was statistically significant based on intensities (Figure 4E).
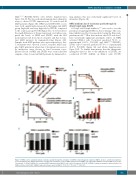
NRF2 mediates Ara-C resistance partly through its direct target gene DUSP1
A Dusp1 and Dusp6 inhibitor,26,27 was used to test the potential of targeting DUSP1 for Ara-C therapy. The com- bined inhibitory effect was predicted using the Bliss inde- pendent model.28,29 Our data indicate that BCI and Ara-C have statistically significant synergistic effects on NRF2 activated SKM-1 cells (%survival, predicted 70.1% vs. experimental 51.0%; P=0.005) and MLLPTD/WT/RUNX1- S291fs cells (%survival, predicted 57.0% vs. experimental 41.0%; P=0.048) (Figure 5A and Online Supplementary Figure S5E). To further demonstrate that the therapeutic synergistic effect is due to the inhibition of DUSP1, we conducted DUSP1 shRNA on SKM-1 cells. DUSP1
AB
C
D
E
Figure 5. NRF2 confers cytarabine (Ara-C) resistance partly through the activation of DUSP1 in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). (A) Ara-C and (E)-2-benzylidene- 3-(cyclohexylamino)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one (BCI) have synergistic effects in NRF2 agonist-treated SKM-1 cells. (B) DUSP1 shRNA-1 sensitized SKM-1 cells to Ara- C treatment. (C) DUSP1 shRNA-1 re-sensitized NRF2 agonist treated SKM-1 cells to Ara-C treatment. (D) DUSP1 shRNA-1 enhanced apoptosis induced by Ara-C in SKM-1 cell lines. (E) DUSP1 shRNA-1 induced S phrase arrest in SKM-1. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P≤0.001.
haematologica | 2019; 104(3)
491