Page 114 - Haematologica3
P. 114
474
X. Wang et al.
or B-cell lymphomas.37 However, we did not detect upreg- ulation of any factors related to interferon responses in Ara-C-damaged primary B cells. This observation is con- sistent with previous findings in 3’ repair exonuclease 1 (Trex 1) conditional knockout mice.38 TREX1 is an exonu- clease that degrades cytosolic DNA and RNA and one of the unknown substrates of TREX1 can trigger cytoplasmic DNA sensor cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS). Loss of Trex1 in dendritic cells was sufficient to cause the release of interferon and systemic autoimmunity, whereas, dele- tion of Trex1 in B cells via CD19Cre did not produce any detectable interferon responses.38 Taken together, these data suggest that primary B cells appear to tolerate DNA damage with a higher threshold than other types of cells. This phenomenon is likely attributed to the physiological process of programmed generation of double-stranded breaks in primary B cells, namely, class switch recombina- tion and somatic hypermutation. Double-stranded breaks are the essential intermediates of class switch recombina- tion,39 and recent studies revealed that somatic hypermu- tation can result in double-stranded break formation in activated B cells.40 Hence, it may not be surprising that
most non-Hodgkin lymphomas (80-90%) derive from B cells (B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma).41 This higher inci- dence of B-cell lymphomas is probably attributable to B- cell-specific DNA recombination induced by activation- induced deaminase.39 While primary B cells do not appear to trigger any immune responses upon DNA damage, this scenario would help to protect DNA-damaged B cells from being attacked by innate immune cells or T cells.
Since Ara-C functions as an S phase-specific chemotherapeutic drug, it would presumably arrest cells in the S phase. We found, however, that different types of B-cell lymphomas were arrested in distinct phases of the cell cycle by Ara-C treatment. The differential cell cycle arrests might depend on the specificity of chemotherapy agents (e.g., Ara-C versus doxorubicin), the severity of induced DNA damage and the genetic or epigenetic pro- files of different types of B-cell lymphomas. Intriguingly, we found that the cell cycle arrest pattern in certain B-cell lymphomas can be shifted with different chemothera- peutic agents. For instance, Ramos and Ly7 were arrested by Ara-C in the G1 or S phase; however, they could be preferentially arrested in the G2 phase by doxorubicin
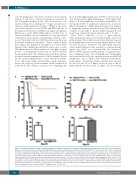
Figure 7. Combined treatment with Wee1 inhibitor (MK1775) and Ara-C eradicates transplanted G1XP lymphoma and attenuates side effects. (A) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of recipient mice inoculated with G1XP lymphomas and treated with vehicle (n=18), Ara-C (n=13), MK1775 (n=13) or both (n=13). Data are combined from three independent experiments. When tumor size reached 4000 mm3 or other humane end points were met (e.g., necrotic tumors), mice were euthanized in accordance with institutional guidelines. (B) Combined treatment with Ara-C and MK1775 profoundly suppressed the growth of G1XP lymphomas. Recipients were treated daily with vehicle control or MK1775 from day 21 until termination, or with Ara-C alone from day 21 to day 46, or Ara-C/MK1775 from day 21 to day 28 after tumor inoculation. (C) Combined treatment remarkably reduced the tumor size. The tumor size was monitored for the group treated with Ara-C alone (n=26) vs. the Ara-C/MK1775 (n=26) treated group for about 1 week (from day 32 to day 38 after tumor inoculation), whereas the vehicle control and MK1775 groups were already terminated. Data are shown for theday 34 time point. (D) The weight of recipient mice was increased in the combined treatment group. The weight of recipient mice was monitored similarly as described in (C) for the group treated with Ara-C alone (n=13) vs. the Ara-C/MK1775 (n=13) group. Data are shown for day 34 time point. Statistical significance was calculated with a T comparison test, ***P≤0.001.
A
B
CD
haematologica | 2018; 103(3)