Page 160 - 2020_07-Haematologica-web
P. 160
C.R. Soderquist et al.
cases. A missense mutation in the cell cycle regulatory gene CDKN2A and a nonsense mutation in TNFAIP3 were detected in one case each.
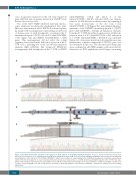
Two of the CD8+ ITLPD exhibited structural chromo- some alterations involving the interleukin-2 (IL2) gene. One case demonstrated an IL2-RHOH (Ras homolog fam- ily member H) rearrangement, representing an inversion of chromosome 4, with breakpoints occurring in the 3’ untranslated region (3’ UTR) of both IL2 (chr4:123372863, c.*44) (Figure 3A) and RHOH (chr4:40246032, c.*449) genes. This rearrangement did not affect the coding sequence, but resulted in the deletion of a portion of the 3’ UTR of IL2, including five of the six AU-rich regulatory elements (ARE, AUUUA). The “reciprocal” RHOH-IL2 rearrangement had breakpoints in the 3’ UTR of RHOH
A
B
C
D
E
F
(chr4:40246006, c.*424) and intron 3 of IL2 (chr4:123373085, c.352-67). Another CD8+ case demon- strated a 1.2 Mb deletion on chromosome 4q, beginning 5 base pairs downstream of the IL2 stop codon (chr4:123372903, c.*5) (Figure 3D) and ending 6 kilobases upstream of the TNFAIP3 interacting protein 3 (TNIP3) gene (chr4:122154953), deleting all regulatory elements from the IL2 3’ UTR. In addition, an inversion, with break- points in exon 4 of IL2 (chr4:123372912, c.457) and intron 2 of TNIP3 (chr4:122128556, c.89+9014) was identified (Figure 3D). A missense mutation in the minichromosome maintenance complex component 5 (MCM5) gene was also identified in this case. The chromosome breakpoints were confirmed in all ITLPD samples with structural IL2 alterations via PCR amplification and Sanger sequencing
Figure 3. Structural chromosome alterations of the IL2 gene in CD8+ indolent T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. In case 7, (A) two chromosome breaks were detected as a consequence of a rearrangement involving the 3’ untranslated region (UTR) of IL2 and 3’ UTR of RHOH (“IL2-RHOH”) and a reciprocal rearrangement involving intron 3 of IL2 and the 3’ UTR of RHOH (“RHOH-IL2”). (B) Pile-up of a subset of reads mapping to the IL2-RHOH rearrangement. (C) Sanger sequencing val- idation of the fusion breakpoints. In case 8, (D) two chromosome breaks were observed due to a 1.2 Mb deletion spanning the majority of the 3’ UTR of IL2 and a portion of the intergenic region between IL2 and TNIP3 (“IL2 3’ UTR del”) and an inversion involving exon 4 of IL2 and intron 2 of TNIP3 (“IL2-TNIP3”). (E) Pile-up of a subset of reads mapping to the IL2 3’ UTR deletion. (F) Sanger sequencing validation of the deletion breakpoints. †Chromosome position based on assembly GRCh37.p13.
1902
haematologica | 2020; 105(7)