Page 122 - 2020_07-Haematologica-web
P. 122
J.N. Fisher et al.
ABC
DEF
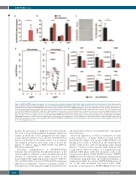
Figure 4. iNUP98-KMT2A expression impairs cell cycle progression of murine embryonic fibroblasts and bone marrow-derived hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. (A) Murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEF), derived from iNUP98-KMT2A and wildtype (WT) control (CTRL) littermate mice were cultured in vitro in the presence of doxycycline (DOX) (1 μg/mL). iNUP98-KMT2A expression is shown relative to the level of GAPDH expression. *P<0.05, unpaired t-test, n=3. (B) Flow cytometry-based cell cycle analysis showed increased G1 and decreased G2/M fractions of in vitro-cultured iNUP98-KMT2A+ MEF compared to WT controls. *P<0.05, unpaired t-test, n=3. (C) iNUP98-KMT2A and WT MEF cultured for eight passages in the presence of DOX (1 μg/mL) were stained for senescence-associated B-galactosidase activity with X-Gal (left panel). The number of X-Gal+ cells in the culture was quantified (right panel). Images and counts are representative of three biological replicates. Scale bars: 100 μm. **P<0.01, unpaired t-test, n=3. (D) Differential mRNA expression from early (passages 1-2) and late (passages 8-10) passaged WT and iNUP98- KMT2A MEF analyzed by a RT2 PCR array. Significant (P<0.05) changes are highlighted in red. (E) Validation of differentially expressed genes in MEF (Figure 4D) by quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis in WT and iNUP98-KMT2A hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells after exposure to DOX (1 μg/mL) in vitro for 48 h. *<0.05, unpaired t-test, n=3.
ly limit the generation of high-titer retroviral particles. We used a doxycycline-regulated transgenic expression system in which the rtTA is integrated into the ubiqui- tously expressed Rosa26 locus and the NUP98-KMT2A fusion is in the Hprt locus under control of a tet-respon- sive minimal promoter, previously used to model the impact of cellular origin in KMT2A-AF9 and KMT2A- ENL-driven leukemia.22,23,27
Secondary transplantation of iNUP98-KMT2A leukemic cells revealed that the inherent leakiness of the system might be sufficient to drive the phenotype in the absence of doxycycline after cellular selection in the mouse (Figure 3D) suggesting that, in contrast to KMT2A- AF9 or KMT2A-ENL, low level NUP98-KMT2A transgene expression is sufficient to exert its oncogenic activity or that expression of the transgene might be required for ini-
tial transformation but not for maintenance of neoplastic cells in all cases.
Retroviral expression, as well as constitutive or condi- tional activation, of many AML-associated fusions [involving the retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA), core binding factor (CBF) or KMT2A] in the hematopoietic system of the mouse often closely phenocopies human disease.28,29 In most of these models, AML develops after a long latency without evidence of a symptomatic pre- leukemic MDS phase, with few exceptions such as the Vav1-promoter driven NUP98-HOXD13 fusion.30 NUP98- HOXD13 mice developed T-cell leukemia, undifferentiat- ed leukemia, megakaryocytic and erythroid leukemia or symptomatic MDS. In contrast, iNUP98-KMT2A mice (5 out of 22) only developed Gr-1+/Mac-1+/c-Kit+ AML. Leukemic transformation of NUP98-HOXD13 mice was
1864
haematologica | 2020; 105(7)