Page 189 - Haematologica - Vol. 105 n. 6 - June 2020
P. 189
PIKfyve inhibition in multiple myeloma
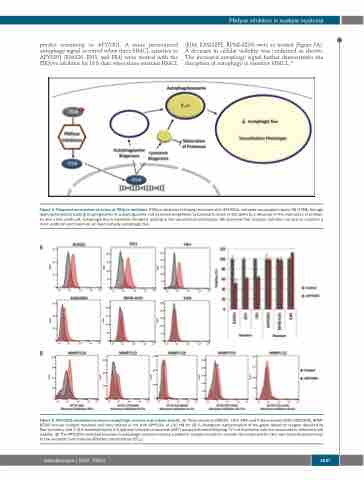
predict sensitivity to APY0201. A more pronounced autophagy signal occurred when three HMCL sensitive to APY0201 (KMS26, JJN3, and FR4) were treated with the PIKfyve inhibitor for 18 h than when three resistant HMCL
(EJM, KMS28PE, RPMI-8226) were so treated (Figure 5A). A decrease in cellular viability was confirmed as shown. The increased autophagy signal further demonstrates the disruption of autophagy in sensitive HMCL.34
Figure 4. Proposed mechanism of action of PIKfyve inhibitors. PIKfyve inhibition following treatment with APY0201, activates transcription factor EB (TFEB) through dephosphorylation leading to upregulation of autophagosome and lysosome biogenesis. Lysosomal function is disrupted by a decrease in the maturation of proteas- es and a less acidic pH. Autophagic flux is therefore disrupted, leading to the vacuolization phenotype. We observed that resistant cell lines are able to maintain a more acidic pH and maintain, at least partially, autophagic flux.
A
B
Figure 5. APY0201-mediated increase in autophagic vesicles and cellular toxicity. (A) Three sensitive (KMS26, JJN3, FR4) and three resistant (EJM, KMS28PE, RPMI- 8226) human multiple myeloma cell lines treated or not with APY0201 at 100 nM for 18 h. Histogram representation of the green detection reagent detected by flow cytometry and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay performed following 72 h of incubation with the compound to determine cell viability. (B) The APY0201-mediated increase in autophagic vesicles in primary patients’ samples treated or not with the compound for 18 h was inversely proportional to the mid-point half maximal effective concentration (EC50).
haematologica | 2020; 105(6)
1647