Page 186 - Haematologica - Vol. 105 n. 6 - June 2020
P. 186
C. Bonolo de Campos et al.
A
B
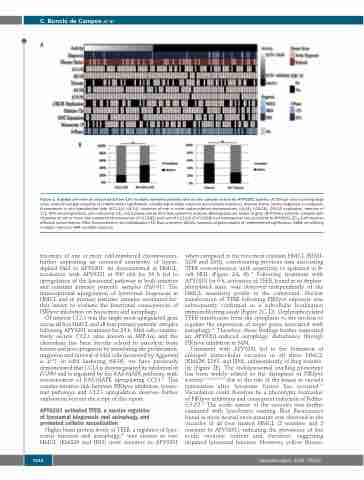
Figure 1. A global overview of clinical data from 100 multiple myeloma patients with ex vivo samples tested for APY0201 activity. (A) Clinical data including diag- nosis (monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, smoldering multiple myeloma and multiple myeloma), disease status (newly diagnosed or relapsed), fluorescence in situ hybridization data (t(11;14), t(6;14), trisomies of one or more odd-numbered chromosomes, t(4;14), t(14;16), CSK1B duplication, deletion of 17p, MYC rearrangements, and monosomy 13), and S-phase status from flow cytometry analysis. Missing data are shown in gray. (B) Primary patients’ samples with trisomies of one or more odd-numbered chromosomes (P=0.0182) and lack of t(11;14) (P=0.0168) had increased ex vivo sensitivity to APY0201. EC50: half maximal effective concentration; FISH: fluorescence in situ hybridization; FC: flow cytometry; MGUS: monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance; SMM: smoldering multiple myeloma; MM: multiple myeloma
trisomies of one or more odd-numbered chromosomes, further supporting an increased sensitivity of hyper- diploid MM to APY0201. As demonstrated in HMCL, incubation with APY0201 at 500 nM for 24 h led to upregulation of the lysosomal pathway in both sensitive and resistant primary patients’ samples (P≤0.01). The transcriptional upregulation of lysosomal biogenesis in HMCL and in primary patients’ samples warranted fur- ther assays to evaluate the functional consequences of PIKfyve inhibition on lysosomes and autophagy.
Of interest CCL3 was the single most upregulated gene across all five HMCL and all four primary patients’ samples following APY0201 treatment for 24 h. MM cells constitu- tively secrete CCL3 (also known as MIP-1α) and the chemokine has been directly related to osteolytic bone lesions and poor prognosis by stimulating the proliferation, migration and survival of MM cells (reviewed by Aggarwal et al.27). In MM harboring t(4;14), we have previously demonstrated that CCL3 is downregulated by inhibition of FGFR3 and is regulated by the RAS-MAPK pathway, with overactivation of RAS-MAPK upregulating CCL3.28 This counter-intuitive link between PIKfyve inhibition, lysoso- mal pathways and CCL3 upregulation deserves further exploration beyond the scope of this report.
APY0201 activated TFEB, a master regulator of lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy, and promoted cellular vacuolization
Higher basal protein levels of TFEB, a regulator of lyso- somal function and autophagy,29 was shown in two HMCL (KMS26 and JJN3) most sensitive to APY0201
when compared to the two most resistant HMCL (RPMI- 8226 and EJM), corroborating previous data associating TFEB overexpression with sensitivity to apilimod in B- cell NHL (Figure 2A, B).12 Following treatment with APY0201 for 6 h, activation of TFEB, found in its dephos- phorylated state, was observed independently of the HMCL sensitivity profile to the compound. Nuclear translocation of TFEB following PIKfyve exposure was subsequently confirmed in a subcellular localization immunoblotting assay (Figure 2C, D). Dephosphorylated TFEB translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus to regulate the expression of target genes associated with autophagy.30 Therefore, these findings further supported an APY0201-induced autophagy disturbance through PIKfyve inhibition in MM.
Treatment with APY0201 led to the formation of enlarged intracellular vacuoles in all three HMCL (KMS26, L363, and EJM), independently of drug sensitiv- ity (Figure 2E). The endolysosomal swelling phenotype has been widely related to the disruption of PIKfyve activity11–13,15,16,26,31 due to the role of the kinase in vacuole maturation after lysosome fusion has occurred.31 Vacuolation could therefore be a phenotypic biomarker of PIKfyve inhibition and consequent reduction of PtdIns- 3,5-P2.14 The acidic nature of the vacuoles was further examined with LysoSensor staining. Blue fluorescence found in more neutral environments was observed in the vacuoles of all four treated HMCL (2 sensitive and 2 resistant to APY0201), indicating the prevalence of less acidic vacuolar content and, therefore, suggesting impaired lysosomal function. However, yellow fluores-
1644
haematologica | 2020; 105(6)