Page 35 - Haematologica May 2020
P. 35
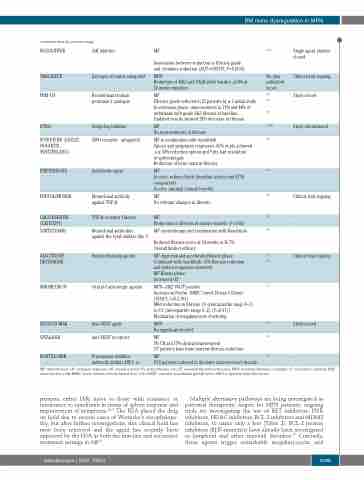
BM niche dysregulation in MPN
continued from the previous page
RUXOLITINIB
TAMOXIFEN
PRM-151
IPI926
SONIDEGIB (LDE225, NOVARTIS, SWITZERLAND)
PIRFENIDONE
FRESOLIMUMAB
GALUNISERTIB
(LY2157299) SIMTUZUMAB
AZACITIDINE DECITABINE
MIRABEGRON
BEVACIZUMAB
VATALANIB
BORTEZOMIB
JAK inhibitor
Estrogen receptor antagonist
Recombinant human pentraxin-2 analogue
Hedgehog inhibitor
SMOreceptor antagonist
Antifibrotic agent
Monoclonal antibody against TGF-β
TGF-β receptor I kinase Monoclonal antibodies
against the Lysyl oxidase like-2
Hypomethylating agents
Oral β-3 adrenergic agonist Anti-VEGF agent
Anti-VEGF receptors
MF
Association between reduction in fibrosis grade
69,97
No data published as yet.
100
101
102
103,104
105
106
107
108
109
110 121
112
113
114
118
Single agent studies closed
Clinical trial ongoing
Study closed
Study discontinued
-
-
Clinical trial ongoing
-
-
Clinical trial ongoing
Study closed
-
-
and cytokines reduction (AUC=0.85939, P=0.0134) MPN
Reduction of JAK2 and CALR allele burden ≥50% at 24 weeks mutation
MF
Fibrosis grade reduced in 25 patients by ≥ 1 initial study. In extension phase, improvements in 71% and 44% of individuals with grade 2&3 fibrosis at baseline.
Updated results showed 28% decrease in fibrosis.
MF
No improvements in fibrosis
MF in combination with ruxolitinib
Spleen and symptoms responses- 65% of pts achieved
a ≥ 50% reduction spleen and 9 pts had resolution of splenomegaly.
Reduction of bone marrow fibrosis
Proteasome inhibitor
MF
In vitro- reduced both fibroblast activity and ECM components
In vivo- minimal clinical benefits.
MF
No relevant changes in fibrosis
MF
Reductions in fibrosis in murine models (P=0.02) MF- monotherapy and combination with Ruxolitinib
Reduced fibrosis score at 24 weeks in 36.7%. Overall limited efficacy
MF- high risk and accelerated/blastic phase. Combined with ruxolitinib- 57% fibrosis reduction and spleen responses observed.
MF-Blastic phase
Increased OS.
MPN- JAK2 V617F positive
Increase in Nestin+ BMSC (week 24 was 3.52/mm2 [95%CI: 1.65-5.39])
Mild reduction in fibrosis 1.0 (interquartile range 0–3) to 0.5 (interquartile range 0–2) (P=0.01))
Modulation of megakaryocyte clustering
MPN
No significant benefit
MF
3% CR and 17% clinical improvement
3/7 patients have bone marrow fibrosis reduction
MF
9/15 patients reduced in the bone marrow vessel density.
indirectly inhibits HIF1- α
MF: myelofibrosis; CR: complete response; OS: overall survival; PV: polycythemia vera; ET: essential thrombocythaemia; MPN: myeloproliferative neoplasm; CI: confidence interval; MNC: mononuclear cells; BMSC: bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells;VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; HIF1-α: hypoxia-inducible factor.
patients, either JAKi naïve or those with resistance or intolerance to ruxolitinib in terms of spleen response and improvement of symptoms.86,87 The FDA placed the drug on hold due to several cases of Wernicke’s encephalopa- thy, but after further investigations, this clinical hold has now been removed and the agent has recently been approved by the FDA in both the first-line and successive treatment settings in MF.88
Multiple alternative pathways are being investigated as potential therapeutic targets for MPN patients; ongoing trials are investigating the use of BET inhibitors, PI3K inhibitors, HDAC inhibitors, BCL-2 inhibitors and MDM2 inhibitors, to name only a few (Table 2). BCL-2 protein inhibitors (BH3-mimetics) have already been investigated in lymphoid and other myeloid disorders.89 Curiously, these agents trigger remarkable megakaryocytic and
haematologica | 2020; 105(5)
1195