Page 207 - Haematologica May 2020
P. 207
BCR/PI3K blockade upregulates CXCR4 in DLBCL
BCR-dependent lines. As expected, none of the com- pounds modulated CXCR4 expression in a BCR-indepen- dent DLBCL cell line (Toledo) (Figure 4A-B).
Consistent with these observations, chemical inhibition of SYK/PI3K was more effective than BTK blockade in augmenting SDF-1α– induced chemotaxis (Figure 5).
Discussion
In this study, we identify CXCR4 upregulation as an indi- cator of sensitivity to targeted inhibition of BCR/PI3K sig- naling in DLBCL cell lines and primary tumor cell suspen- sions. Chemical SYK inhibition, genetic SYK depletion and PI3K inhibition all increased CXCR4 expression in BCR- dependent DLBCLs. In DLBCLs with low or high baseline NF-κB, CXCR4 expression was modulated in a PI3K/AKT/FOXO1-dependent manner at the level of tran- scription (Figure 6). In addition to enhanced CXCR4 expres- sion, proximal BCR(SYK)/PI3K inhibition induced chemo- taxis of DLBCL cell lines to the CXCR4 ligand, SDF-1α.
In the current studies, we find induction of CXCR4 at the transcript level within 6 h of proximal BCR signaling block- ade. Thereafter, increased CXCR4 cell surface expression is readily detectable by flow cytometry within 24 h of SYK or PI3K inhibition in almost all BCR-dependent DLBCLs. In recent studies, PI3K/mammalian target of rapamycin chem- ical inhibition also increased CXCR4 transcript abundance
31
in BCR-dependent DLBCL cell lines. Taken together, these
data suggest that CXCR4 upregulation is an indicator of sensitivity to inhibition of proximal BCR/PI3K signaling in DLBCLs.
CXCR4 is a FOXO1 target gene which, under physiolog- ical conditions, contributes to the polarization of light zone and dark zone GC-B cells.13 Upon inhibition of the BCR/SYK/PI3K/AKT axis, FOXO1 is dephosphorylated and retained in the nucleus, initiating transcription of its tar- get genes.8 FOXO1 is considered to be a homeostatic regu- lator with targets that include pro-apoptotic mediators of cell death such as BIM, HRK or p27, as well as BCR/PI3K signaling pathway components including SYK, PIK3CA and CXCR4.1,3,13 Therefore, FOXO1-dependent upregulation of CXCR4 can be regarded as a potential compensatory signal- ing pathway in DLBCLs following proximal BCR/PI3K inhibition.
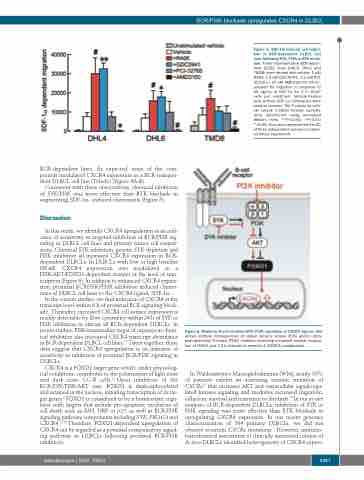
Figure 5. SDF-1α induced cell migra- tion in BCR-dependent DLBCL cell lines following SYK, PI3K or BTK inhibi- tion. Three representative BCR-depen- dent DLBCL lines (DHL4, DHL6 and TMD8) were treated with vehicle, 1 mM R406, 0.5 μM GDC-0941, 0.1 mM PCI- 32765 or 10 mM AMD3100 for 24 (h), assayed for migration in response to 25 ng/mL of SDF-1α for 2 h (2x105 cells per condition). Vehicle-treated cells without SDF-1α stimulation were used as controls. The P-values for vehi- cle versus inhibitor-treated samples were determined using one-tailed Welch’s t-test. **P<0.001; *P<0.01; #P<0.05. Error bars represented the SD of three independent assays in a repre- sentative experiment.
Figure 6. Model for B-cell receptor/SYK/PI3K regulation of CXCR4 signals. Red arrows indicate consequences of spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) and/or phos- phatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibition including increased nuclear localiza- tion of FOXO1 and C-X-C chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) upregulation.
In Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia (WM), nearly 30% of patients exhibit an activating somatic mutation of CXCR432 that increases AKT and extracellular signal-regu- lated kinases signaling and mediates increased migration, adhesion, survival and resistance to ibrutinib.24 In our in vitro analyses of BCR-dependent DLBCLs, inhibition of SYK or PI3K signaling was more effective than BTK blockade in upregulating CXCR4 expression. In our recent genomic characterization of 304 primary DLBCLs, we did not observe recurrent CXCR4 mutations.1 However, immuno- histochemical assessment of clinically annotated cohorts of de novo DLBCLs identified heterogeneity of CXCR4 expres-
haematologica | 2020; 105(5)
1367