Page 204 - Haematologica May 2020
P. 204
L. Chen et al.
and sensitive to chemical SYK inhibition (R406) and molecular depletion of SYK (Online Supplementary Figure S2). Consistent with its designation as an ABC-type DLBCL cell line, TMD8 exhibited high baseline expres- sion of the NF-κB target, BCL2A1, that was markedly reduced following SYK depletion (Online Supplementary Figure S2). The extended cell line panel also included three BCR-independent DLBCL cell lines, K422, Toledo and LY4.3
In the DLBCL cell line panel, chemical SYK inhibition with R406 selectively increased CXCR4 transcript levels in all six BCR-dependent DLBCL cell lines; however, the baseline CXCR4 levels in HBL1 were low. Chemical SYK inhibition did not modulate CXCR4 transcript abundance in the three BCR-independent DLBCL cell lines (Figure 1A, top panel). Similar results were obtained with a more selective chemical SYK inhibitor, GS-9973, that is current- ly under evaluation in lymphoma clinical trials (Figure 1A, lower panel).26-28
SYK depletion with three independent shRNAs signifi- cantly increased CXCR4 transcripts in BCR-dependent, but not BCR-independent DLBCL cell lines, phenocopying the CXCR4 induction following chemical SYK inhibition (Figure 1B). Consistent with these findings, chemical inhi- bition of SYK with either R406 or GS-9973 selectively increased cell surface CXCR4 protein expression in the BCR-dependent DLBCLs (with the least effect in HBL1), but not in the BCR-independent DLBCLs (Figure 1C, R406, top panel; GS-9973, bottom panel).
After identifying selective CXCR4 induction in BCR- dependent DLBCLs cell lines, we assessed the same parameters in primary DLBCLs. For these studies, we uti-
A
lized aliquots of six cryopreserved viable tumor suspen- sions of primary DLBCL that were previously character- ized as BCR-dependent with low baseline NF-κB activity (P1 and P2), BCR-dependent with high baseline NF-κB activity (P3 and P4); or BCR-independent (P5 and P6).3 As in the DLBCL cell lines, chemical SYK inhibition selective- ly induced CXCR4 in all four BCR-dependent primary DLBCLs (P1-P4) but not in the two BCR-independent pri- mary DLBCLs (P5 and P6) (Figure 1D).
Prolonged chemical SYK inhibition increases SDF-1α associated migration of BCR-dependent DLBCLs
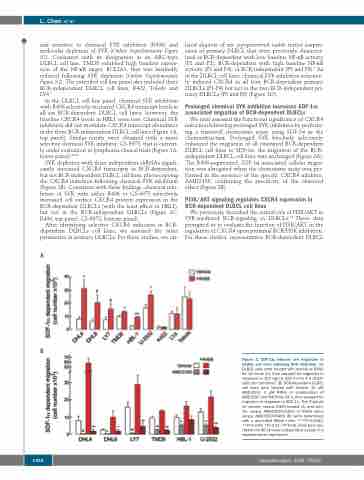
We next assessed the functional significance of CXCR4 induction following prolonged SYK inhibition by perform- ing a transwell chemotaxis assay using SDF-1α as the chemoattractant. Prolonged SYK blockade selectively enhanced the migration of all examined BCR-dependent DLBCL cell lines to SDF-1α; the migration of the BCR- independent DLBCL cell lines was unchanged (Figure 2A). The R406-augmented, SDF-1α associated cellular migra- tion was abrogated when the chemotaxis assay was per- formed in the presence of the specific CXCR4 inhibitor, AMD3100, confirming the specificity of the observed effect (Figure 2B).
PI3K/AKT signaling regulates CXCR4 expression in BCR-dependent DLBCL cell lines
We previously described the central role of PI3K/AKT in SYK-mediated BCR-signaling in DLBCLs.3,9 These data prompted us to evaluate the function of PI3K/AKT in the regulation of CXCR4 upon proximal BCR/PI3K inhibition. For these studies, representative BCR-dependent DLBCL
B
Figure 2. SDF-1α induced cell migration in DLBCL cell lines following SYK inhibition. (A) DLBCL cells were treated with vehicle or R406 for 24 hours (h), then assayed for migration in response to 100 ng/mL SDF-1α for 4 h (2x105 cells per condition). (B) BCR-dependent DLBCL cell lines were treated with vehicle, 10 mM AMD3100, 1 mM R406 or combination of AMD3100 and R406 for 24 h, then assayed for migration in response to SDF-1α. The P-values for vehicle- versus R406-treated (A) and vehi- cle- versus AMD3100-treated or R406 alone versus AMD3100+R406 (B) were determined with a one-sided Welch t-test. ***P<0.0001; **P<0.001; *P<0.01; #P<0.05. Error bars rep- resent the SD of three independent assays in a representative experiment.
1364
haematologica | 2020; 105(5)