Page 90 - Haematologica April 2020
P. 90
Y. Xie et al.
genotype showed consistently reduced phosphorylated p38 in pro-erythroblasts (Figure 6C and D). Similar to the case of arhgef12 MO, where the p38 activity is inhibited in the zebrafish, these rs10892563 CC genotype patients showed an erythroid differentiation block at the erythrob- last stage (Figure 6A and B), suggesting a strong associa- tion with the ARHGEF12-p38 pathway.
Discussion
For leukemia patients, hematologic toxicity is the most common side effect of chemotherapy as the hematopoiet-
ic cells are among the tissues most vulnerable to therapy- related damage, in part due to their active cell cycle status. Anemia is one of the most frequently recorded manifesta- tions of the hematopoietic toxic effects during the course of chemotherapy. Chemotherapy-induced anemia can be caused by cytotoxic inhibition of normal hematopoiesis similar to chemotherapy-induced neutropenia and throm- bocytopenia. Chemotherapy agent-related autoimmune hemolysis31,32 and chemotherapy-induced eryptosis can also cause anemia.33 Our current GWAS studies have found that chemotherapy-induced anemia is associated with SNP in CHPT1,6 BSG,11,12 ANAX7,14 EPB42,15,16 and ABCC417 that may be related to increased erythrocyte
A
B
C
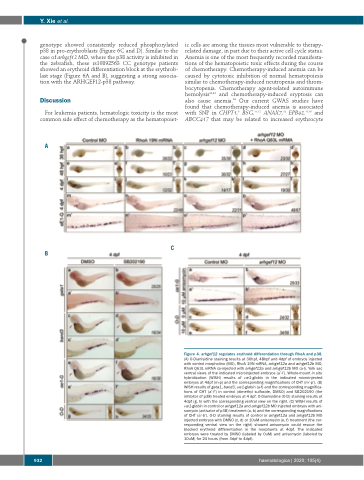
Figure 4. arhgef12 regulates erythroid differentiation through RhoA and p38. (A) O-Dianisidine staining results at 36hpf, 48hpf and 4dpf of embryos injected with control morpholino (MO), RhoA 19N mRNA, arhgef12a and arhgef12b MO, RhoA Q63L mRNA co-injected with arhgef12a and arhgef12b MO (a-l). Yolk sac ventral views of the indicated microinjected embryos (a’-l’). Whole-mount in situ hybridization (WISH) results of αe1-globin in the indicated microinjected embryos at 4dpf (m-p) and the corresponding magnifications of CHT (m’-p’). (B) WISH results of gata1, band3, αe1-globin (a-f) and the corresponding magnifica- tions of CHT (a’-f’) in control (dimethyl sulfoxide, DMSO) and SB202190 (the inhibitor of p38) treated embryos at 4 dpf. O-Dianisidine (O-D) staining results at 4dpf (g, h) with the corresponding ventral view on the right. (C) WISH results of αe1-globin in control or arhgef12a and arhgef12b MO injected embryos with ani- somycin (activator of p38) treatment (a, b) and the corresponding magnifications of CHT (a’-b’). O-D staining results of control or arhgef12a and arhgef12b MO injected embryos with DMSO (c, d) or 10uM anisomycin (e, f) treatment (the cor- responding ventral view on the right) showed anisomycin could rescue the blocked erythroid differentiation in the morphants at 4dpf. The indicated embryos were treated by DMSO (labeled by 0uM) and anisomycin (labeled by 10uM) for 24 hours (from 3dpf to 4dpf).
932
haematologica | 2020; 105(4)