Page 67 - Haematologica April 2020
P. 67
RUNX3 in aging and erythroid-myeloid balance
and D). Datasets for H3K27ac in young versus aged murine HSC are not currently available. The human RUNX3 locus showed aging-associated decreases in H3K27ac within the P2 promoter, as well as the super-enhancer region located approximately 97 kilobases upstream of the P2 promot- er28 (GSE104406) (Figure 1E-G).
RUNX3 in human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells participates in erythroid programming
The decline in HSC RUNX3 levels with aging illustrated in Figure 1A raised questions about potential roles in human hematopoietic differentiation. Human CD34+ HSPC cultures were used to examine protein expression
A
B
CDE
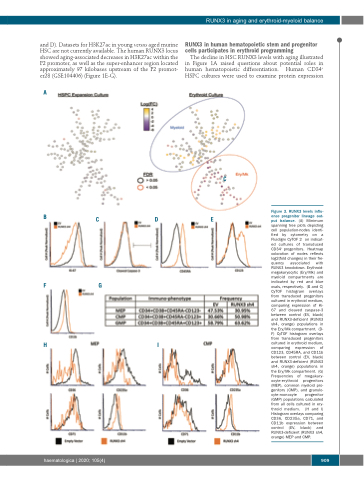
Figure 3. RUNX3 levels influ- ence progenitor lineage out- put balance. (A) Minimum spanning tree plots depicting cell population-nodes identi- fied by cytometry on a Fluidigm CyTOF 2 on indicat- ed cultures of transduced CD34+ progenitors. Heatmap coloration of nodes reflects log2(fold changes) in their fre- quency associated with RUNX3 knockdown. Erythroid- megakaryocytic (Ery/Mk) and myeloid compartments are indicated by red and blue ovals, respectively. (B and C) CyTOF histogram overlays from transduced progenitors cultured in erythroid medium, comparing expression of Ki- 67 and cleaved caspase-3 between control (EV, black) and RUNX3-deficient (RUNX3 sh4, orange) populations in the Ery/Mk compartment. (D- F) CyTOF histogram overlays from transduced progenitors cultured in erythroid medium, comparing expression of CD123, CD45RA, and CD11b between control (EV, black) and RUNX3-deficient (RUNX3 sh4, orange) populations in the Ery/Mk compartment. (G) Frequencies of megakary- ocyte-erythroid progenitors (MEP), common myeloid pro- genitors (CMP), and granulo- cyte-monocyte progenitor (GMP) populations calculated from all cells cultured in ery- throid medium. (H and I) Histogram overlays comparing CD36, CD235a, CD71, and CD11b expression between control (EV, black) and RUNX3-deficient (RUNX3 sh4, orange) MEP and CMP.
FG
HI
C
haematologica | 2020; 105(4)
909