Page 249 - Haematologica April 2020
P. 249
The role of neuraminidases in platelet function
in the A1 domain of VWF are critical for binding to GPIbα.43 When sialic acid is cleaved from O-linked glycan structures, galactose-residues originally bound to GalNAc and GlcNac-residues become exposed, in contrast to N- linked glycans, where sialic acid is attached only to galac- tose residues. Additionally, the β3-domain of αIIbβ3-integrin
also contains N-linked glycans45 and the majority of these structures are rich in mannose. It is currently unclear whether other platelet glycoproteins or plasma proteins (e.g. alpha2 macroglobulin) are affected by NEU. However platelet stimulation with other agonists did not lead to an increase in membrane-associated NEU.
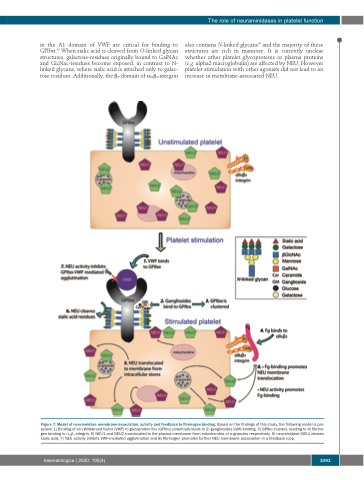
Figure 7: Model of neuramidase membrane-association, activity and feedback to fibrinogen binding. Based on the findings of this study, the following model is pro- posed: 1) Binding of von Willebrand factor (VWF) to glycoprotein Ibα (GPIbα) potentially leads to 2) gangliosides (GM) binding, 3) GPIbα clusters, leading to 4) fibrino- gen binding to αIIbβ3-integrin, 5) NEU1 and NEU2 translocated to the plasma membrane from mitochondria or α-granules respectively, 6) neuramidase (NEU) cleaves sialic acid, 7) NEU activity inhibits VWF-mediated agglutination and 8) fibrinogen promotes further NEU membrane association in a feedback loop.
haematologica | 2020; 105(4)
1091