Page 160 - Haematologica April 2020
P. 160
V.P. Vaikari et al.
S3A). Based on leukemia cytogenetics, no significant dif- ferences in CD99 expression was found in patients with complex karyotype, Inv (16), t (15; 17), t (8,21), del (7q) / 7q- and trisomy 8, compared with normal karyotype (Online Supplementary Figure S3B).
CD99 overexpression is associated with better clinical outcome
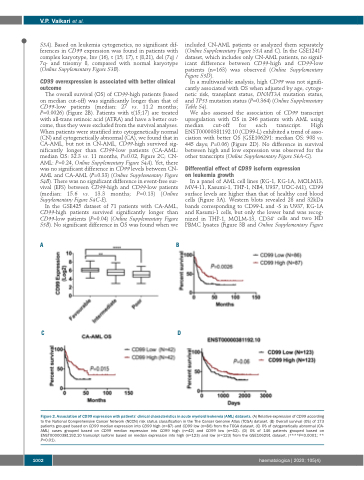
The overall survival (OS) of CD99-high patients (based on median cut-off) was significantly longer than that of CD99-low patients (median: 27 vs. 11.2 months; P=0.0026) (Figure 2B). Patients with t(15;17) are treated with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and have a better out- come, thus they were excluded from the survival analyses. When patients were stratified into cytogenetically normal (CN) and cytogenetically abnormal (CA), we found that in CA-AML, but not in CN-AML, CD99-high survived sig- nificantly longer than CD99-low patients (CA-AML: median OS: 32.3 vs. 11 months, P=0.02, Figure 2C; CN- AML: P=0.24, Online Supplementary Figure S4A). Yet, there was no significant difference in CD99 levels between CN- AML and CA-AML (P=0.33) (Online Supplementary Figure S4B). There was no significant difference in event-free sur- vival (EFS) between CD99-high and CD99-low patients (median: 15.6 vs. 13.3 months; P=0.13) (Online Supplementary Figure S4C-E).
In the GSE425 dataset of 71 patients with CA-AML, CD99-high patients survived significantly longer than CD99-low patients (P=0.04) (Online Supplementary Figure S5B). No significant difference in OS was found when we
AB
included CN-AML patients or analyzed them separately (Online Supplementary Figure S5A and C). In the GSE12417 dataset, which includes only CN-AML patients, no signif- icant difference between CD99-high and CD99-low patients (n=163) was observed (Online Supplementary Figure S5D).
In a multivariable analysis, high CD99 was not signifi- cantly associated with OS when adjusted by age, cytoge- netic risk, transplant status, DNMT3A mutation status, and TP53 mutation status (P=0.364) (Online Supplementary TableS4).
We also assessed the association of CD99 transcript upregulation with OS in 246 patients with AML using median cut-off for each transcript. High ENST00000381192.10 (CD99-L) exhibited a trend of asso- ciation with better OS (GSE106291: median OS: 908 vs. 445 days; P=0.06) (Figure 2D). No difference in survival between high and low expression was observed for the other transcripts (Online Supplementary Figure S6A-G).
Differential effect of CD99 isoform expression on leukemia growth
In a panel of AML cell lines (KG-1, KG-1A, MOLM13, MV4-11, Kasumi-1, THP-1, NB4, U937, UOC-M1), CD99 surface levels are higher than that of healthy cord blood cells (Figure 3A). Western blots revealed 28 and 32kDa bands corresponding to CD99-L and -S in U937, KG-1A and Kasumi-1 cells, but only the lower band was recog- nized in THP-1, MOLM-13, CD34+ cells and two HD PBMC lysates (Figure 3B and Online Supplementary Figure
CD
Figure 2. Association of CD99 expression with patients’ clinical characteristics in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) datasets. (A) Relative expression of CD99 according to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) risk status classification in the The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset. (B) Overall survival (OS) of 173 patients grouped based on CD99 median expression into CD99 high (n=87) and CD99 low (n=86) from the TCGA dataset. (C) OS of cytogenetically abnormal (CA- AML) cases grouped based on CD99 median expression into CD99 high (n=42) and CD99 low (n=42). (D) OS of 146 patients grouped based on ENST00000381192.10 transcript isoform based on median expression into high (n=123) and low (n=123) from the GSE106291 dataset. (****P<0.0001; ** P<0.01).
1002
haematologica | 2020; 105(4)