Page 152 - Haematologica April 2020
P. 152
L. Boutin et al.
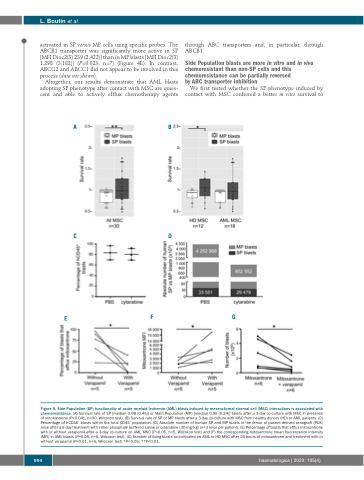
activated in SP versus MP cells using specific probes. The ABCB1 transporter was significantly more active in SP [MFI Dioc2(3) 239 (2,422)] than in MP blasts [MFI Dioc2(3) 1,298 (3,182)] (P=0.023, n=7) (Figure 4E). In contrast, ABCG2 and ABCC1 did not appear to be involved in this process (data not shown).
Altogether, our results demonstrate that AML blasts adopting SP phenotype after contact with MSC are quies- cent and able to actively efflux chemotherapy agents
through ABC transporters and, in particular, through ABCB1.
Side Population blasts are more in vitro and in vivo chemoresistant than non-SP cells and this chemoresistance can be partially reversed
by ABC transporter inhibition
We first tested whether the SP phenotype induced by contact with MSC conferred a better in vitro survival to
E
FG
AB
CD
Figure 5. Side Population (SP) functionality of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) blasts induced by mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) interactions is associated with chemoresistance. (A) Survival rate of SP [median 0.98 (0.46)] or Main Population (MP) [median 0.95 (0.24)] blasts after a 3-day co-culture with MSC in presence of mitoxantrone (P=0.041, n=30, Wilcoxon test). (B) Survival rate of SP or MP blasts after a 3-day co-culture with MSC from healthy donors (HD) or AML patients. (C) Percentage of hCD45+ blasts within the total CD45+ population. (D) Absolute number of human SP and MP blasts in the femur of patient-derived xenograft (PDX) mice after a 5-day treatment with either phosphate buffered saline or cytarabine (30 mg/kg) (n=3 mice per patient). (E) Percentage of blasts that efflux mitoxantrone with or without verapamil after a 3-day co-culture on AML MSC (P=0.05, n=5, Wilcoxon test) and (F) the corresponding mitoxantrone mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) in AML blasts (P=0.05, n=5, Wilcoxon test). (G) Number of living blasts co-cultivated on AML or HD MSC after 24 hours of mitoxantrone and treatment with or without verapamil (P=0.01, n=6, Wilcoxon test) *P<0.05; **P<0.01.
994
haematologica | 2020; 105(4)