Page 120 - Haematologica March 2020
P. 120
L. de Swart et al.
analysis was performed in the survival regressions to take into account that the population was not homogeneous but distributed over different centers in several countries, using a random effects frailty term. The random effect, called “frailty”, is the term that describes the common risk or the individual heterogeneity, acting as a factor on the hazard function. Missing values in adjustment variables were imputed with last observation carried forward or next observation carried backward.
Results
Patients’ characteristics
The EUMDS Registry contained data from 2,192 patients diagnosed between December 3, 2007 and March
14, 2017 of whom 1,504 patients had data recorded from three or more visits (visit 3 = landmark at the 1-year fol- low-up). Two patients with refractory anemia with excess blasts-2 were excluded, resulting in the inclusion of 1,502 patients. An additional 235 patients were excluded, as one or more of the following variables had never been meas- ured or the test failed throughout the study: cytogenetics (n=112), EQ-5D (n=101), blast count (n=60), platelet count (n=1), and neutrophil count (n=2). The final cohort con- sisted of 1,267 patients, unselected for any type of treat- ment. In 162 patients the disease had progressed to high- er-risk MDS or acute myeloid leukemia and 317 patients had died without progression. The median survival after disease progression was 5.3 months [95% confidence interval (95% CI); 3.2- 9.8 months]. Full details of the
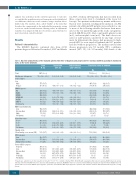
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the included patients from time of diagnosis and progression-free survival, stratified according to transfusion status at the visit 3 landmark.
Total N. (%)
1267 (100.0)
73.0 (18.0 - 95.0)
757 (59.7) 510 (40.3)
218 (17.2) 214 (16.9) 492 (38.8) 86 (6.8) 133 (10.5) 41 (3.2) 83 (6.6)
782 (61.7) 411 (32.4) 71 (5.6) 3 (0.2)
881 (69.5) 210 (16.6) 10 (0.8) 166 (13.1)
70.5 (19.7)
680 (53.7) 557 (44.0) 30 (2.4)
386 (30.5) 571 (45.1) 204 (16.1) 39 (3.1)
3 (0.2)
64 (5.1)
Hazard ratio (95% CI)
1.03 (1.02 - 1.04)
1
0.84 (0.70 - 1.01)
0.84 (0.64 - 1.10) 0.73 (0.56 - 0.96) 1
1.03 (0.72 - 1.46) 1.58 (1.20 - 2.07) 0.64 (0.34 - 1.22) 0.61 (0.40 - 0.92)
1
1.24 (1.02 - 1.50) 1.55 (1.08 - 2.22) -
1
1.72 (1.38 - 2.15) 2.04 (0.76 - 5.48) 1.08 (0.80 - 1.45)
0.99 (0.98 - 0.99)
1
1.95 (1.62 - 2.34) 0.83 (0.43 - 1.62)
1
1.80 (1.41 - 2.29) 3.19 (2.41 - 4.22) 4.27 (2.72 - 6.71) 3.15 (0.78 - 12.82) 1.69 (1.07 - 2.68)
Adjusted hazard ratio* (95% CI)
1.03 (1.02 - 1.04)
1
0.76 (0.62 - 0.92)
0.78 (0.59 - 1.03) 0.59 (0.45 - 0.78) 1
0.91 (0.64 - 1.30) 1.86 (1.41 - 2.46) 0.68 (0.36 - 1.29) 0.54 (0.35 - 0.83)
1
1.08 (0.88 - 1.31) 1.30 (0.90 - 1.89) -
1
1.40 (1.10 - 1.77) 1.89 (0.69 - 5.15) 0.99 (0.73 - 1.34)
0.99 (0.99 - 1.00)
1
1.71 (1.39 - 2.11) 0.74 (0.38 - 1.45)
1
1.85 (1.45 - 2.37) 3.40 (2.55 - 4.52) 4.59 (2.91 - 7.22) 4.65 (1.13 - 19.15) 1.76 (1.11 - 2.80)
Transfusion status at landmark
Total
Median age at diagnosis,
years (range)
Sex Male Female
WHO diagnosis: RA
RARS RCMD RCMD-RS RAEB-1 MDS-U Deletion 5q
MDS Comorbidity Index Low
Intermediate High
Not known
Karnofsky status 80-100
50-70
10-40
Not known
Quality of life
Visual analog score, mean (SD)
IPSS category Low
Intermediate
Cytogenetics not done
Revised IPSS category Very low
Low
Intermediate
High
Very high Not known
No
751 (100.0)
73.0 (18.0 - 91.0)
445 (59.3) 306 (40.7)
139 (18.5) 123 (16.4) 296 (39.4) 47 (6.3) 78 (10.4) 27 (3.6) 41 (5.5)
482 (64.2) 232 (30.9) 35 (4.7) 2 (0.3)
543 (72.3) 93 (12.4) 3 (0.4) 112 (14.9)
73.1 (18.9)
460 (61.3) 274 (36.5) 17 (2.3)
310 (41.3) 309 (41.1) 89 (11.9) 11 (1.5) 1 (0.1) 31 (4.1)
Yes
516 (100.0)
73.0 (21.0 - 95.0)
312 (60.5) 204 (39.5)
79 (15.3) 91 (17.6) 196 (38.0) 39 (7.6) 55 (10.7) 14 (2.7) 42 (8.1)
300 (58.1) 179 (34.7) 36 (7.0) 1 (0.2)
338 (65.5) 117 (22.7) 7 (1.4) 54 (10.5)
66.8 (20.2)
220 (42.6) 283 (54.8) 13 (2.5)
76 (14.7) 262 (50.8) 115 (22.3) 28 (5.4)
2 (0.4)
33 (6.4)
*Hazard ratio adjusted for all other variables in the table. 95% CI: 95% confidence Interval; WHO: World Health Organization; RA: refractory anemia; RARS: refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts, RCMD: refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia; RCMD-RS: refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia & ring sideroblasts; RAEB: refractory anemia with excess blasts; MDS-U: myelodysplastic syndrome, unclassifiable; MDS: myelodysplastic syndrome; SD: standard deviation; IPSS: International Prognostic Scoring System.
634
haematologica | 2020; 105(3)