Page 215 - Haematologica Atlas of Hematologic Cytology
P. 215
CHAPTER 25 - Inherited hemoglobin disorders
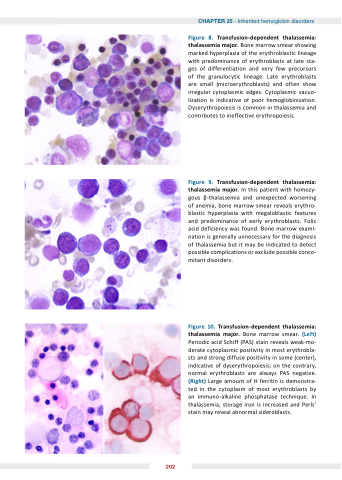
Figure Transfusion dependent thalassemia thalassemia major Bone marrow smear showing marked hyperplasia of the erythroblastic lineage with predominance of erythroblasts at at late sta- ges of differentiation and very few precursors of the granulocytic lineage Late erythroblasts are small (microerythroblasts) and often show irregular cytoplasmic edges Cytoplasmic vacuo- lization is indicative of poor hemoglobinization Dyserythropoiesis is is common in thalassemia and contributes to ineffective erythropoiesis Figure Transfusion dependent thalassemia thalassemia major In this patient with homozy- gous -thalassemia and unexpected worsening of anemia bone marrow smear reveals erythro- blastic blastic hyperplasia with megaloblastic features and predominance of early erythroblasts Folic acid deficiency was found Bone marrow exami- nation is is generally unnecessary for the diagnosis of thalassemia but it may be indicated to detect possible possible complications or exclude possible possible conco- mitant disorders
Figure 10 Transfusion dependent thalassemia thalassemia major Bone marrow smear (Left) Periodic acid Schiff (PAS) stain reveals weak-mo- derate cytoplasmic positivity in most erythrobla- sts and strong diffuse positivity in some (center) indicative of dyserythropoiesis on on the contrary normal erythroblasts are always PAS negative (Right) Large amount of H ferritin is demonstra- ted in the cytoplasm of most erythroblasts by an immuno-alkaline phosphatase technique In thalassemia storage iron is increased and Perls stain may reveal abnormal sideroblasts 202