Page 200 - 2019_12-Haematologica-web
P. 200
B. de la Morena-Barrio et al.
quency of 7.5% or 4.32 cases/1000-patient years. As thrombotic events in children are unusual, further investi- gations are nearly always performed. As a result, 54.8% of pediatric patients included in our study were the probands of the affected families (40 of 73). At first thrombotic event, 15 of the patients were neonates, one was an infant, eight were children and 49 were adolescents (Figure 2). Almost half of these events were provoked by additional risk factors (35 of 73, 47.9%) and mainly in ado- lescents (25 of 35, 71.4%) (Table 1). A detailed description of all 73 cases is shown in Online Supplementary Table S1.
Analysis by sex showed a slightly higher incidence of thrombotic events in males than in females (54.8% vs. 45.2%, respectively) (Table 1). This difference was even more pronounced when considering thrombosis at early age: 10 out of 15 neonates with thrombosis (66.7%) were male (Online Supplementary Table S1). When restricting the analysis to children under the age of 11 years, thus excluding the role of estrogen-associated thrombosis, males showed a significantly higher risk for the develop- ment of pediatric thrombosis than females (OR 3.2; 95%CI: 1.3-78; P=0.012). These differences in thrombo-
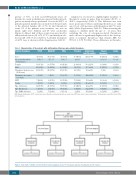
Table 1. Characteristics of the patients with antithrombin deficiency and pediatric thrombosis.
Pediatric thrombosis SPAIN BELGIUM TOTAL Provoked Antithrombin
(anti-FXa activity)
Unusual Deaths thrombosis
Cases 37 (6.1%) 36 (10.1%) 73 (7.5%) 35 (47.9%) 52.3±10.8%
17 (23.3%) 6 (8.2%)
Ageatfirstthrombotic 11.4±7 11.5±7 11.4±7 12.4±7 - 2.6±5.3 5.6±8 event (years)
Females
Males
Thrombosis in adolescence (12-18 years)
Thrombosis in neonates
(< 30 days) CSVT
Deaths
Type I deficiency Type II deficiency
Type II HBS deficiency
13 (35.1%) 24 (64.9%) 25 (66.7%)
6 (16.2%)
7 (18.9%) 5 (13.5%) 32 (86.5%) 5 (13.5%)
1 (2.8%)
20 (55.5%) 16 (44.5%) 24 (66.7%)
9 (25%)
6 (16.7%) 1 (2.8%) 24 (66.7%) 9 (25.7%)
7 (19.4%)
33 (45.2%) 40 (54.8%) 49 (67.1%)
15 (20.5%)
13 (17.8%) 6 (8.2%) 56 (76.7%) 14 (19.2%)
8 (11.0%)
21 (63.6%) 14 (35%) 25 (51%)
8 (53.3%)
7 (53.8%) 2 (33.3%) 27 (48.2%) 6 (42.8%)
2 (25%)
53.0±12.5% 51.7 ±9.2% 52.3±8.5%
46.2±13.4%
51.5±9.2% 41.0±19.0% 52.2±9.7% 50.2±15.4% 45±19.4%
6 (18.8%) 11 (27.5%) 1 (2%)
11 (73.3%)
13 (100%) 2 (33.3%) 11 (19.6%) 6 (42.8%) 1 (12.5%)
3 (9.1%) 3 (7.5%) 1 (2.0%)
3 (20%)
1 (16.6%) -
3 (5.4%) 3 (21.4%) 2 (25%)*
HBS: heparin binding site; CSVT: cerebral sinovenous thrombosis. Unusual thrombosis: renal veins, CSVT, deep veins of upper extremities; *Both patients carried the p.Leu131Phe in homozygosis.
Figure 1. Flow chart of children selected from the entire population. A total of 73 pediatric patients: 40 probands and 33 relatives.
2514
haematologica | 2019; 104(12)