Page 136 - 2019_12-Haematologica-web
P. 136
M. Boudny et al.
A
B
C
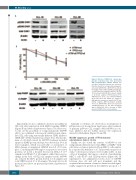
Figure 4. Effects of MU380 in chronic lym- phocytic leukemia (CLL) cells pre-treated with pro-proliferative stimuli. Primary CLL cells were cultured in the presence of pro-pro- liferative stimuli for ten days and subsequent- ly treated with MU380. (A) MU380 [1 μM; 24 hours (h)] enhanced RS (pS345) and abrogat- ed CHK1 protein activation (pS296). (B) The 72-h treatment with MU380 reduced viability of all tested samples; TP53-mutated (n=7), ATM-mutated (n=3) and TP53-wt/ATM-wt (n=3). The effect was similar (IC50 approx. 1 μM) with the exception of sample CLL-75 har- boring complete ATM inactivation (viability 66% at 1 μM MU380). Error bars represent standard deviation. (C) The 48 h treatment with 1 μM MU380 led to cleavage of PARP protein (C-PARP) in the tested samples.
Similarly to cell lines, we observed no accumulation of p53 protein or its downstream target genes after treatment of primary (p53-wt) CLL samples with MU380; in con- trast, inhibitor did not further increase the expression elicited by fludarabine (Figure 5G and H).
MU380 suppresses growth of TP53-mutated subcutaneous tumors in vivo
Finally, we also tested the activity of MU380 in vivo using immunodeficient mice strain NOD-scid IL2Rgnull with subcutaneous tumors generated from MEC-1 cells similar- ly as reported by Attianese et al.40 In line with our previous study,41 subcutaneous tumors were readily visible on day +14 post transplant; the tumors consisted of proliferating MEC-1 cells (Ki-67- and CD20-positive) (Figure 6A). In experiment I, we administered seven doses of MU380 between days +14 and +28 post transplant, and the sequential measurement of tumor volume revealed signif- icantly suppressed growth in the inhibitor group (n = 7
Importantly, we also confirmed a decrease in viability in CLL cells after transfection with siRNA targeting CHEK1 (Figure 5F and Online Supplementary Figure S13). Moreover, to rule out the possibility of compound-specific MU380 effects, we confirmed a decrease in viability in non-stimu- lated CLL cells using structurally different CHK1 inhibitor CHIR-12439 (Online Supplementary Figure S14). The mecha- nism of cell death caused by MU380 treatment included apoptosis (PARP protein cleavage was detected in 19 of 22 tested samples), which was probably a consequence of DNA damage accumulation (gH2AX rise in 8 of 10 sam- ples). Concerning MU380 impact on apoptosis-associated proteins, we noted a frequent decrease in MCL1 (7 of 9 samples) and NF-κB (7 of 12 samples), whilst there was no change in the level of BCL2 (12 samples tested). MU380 also reduced the MYC protein level in 4 of 6 samples and total CHK1 level in 17 of 23 samples. Western blots for all proteins listed above are presented in Online Supplementary Figure S15.
2450
haematologica | 2019; 104(12)