Page 113 - 2019_12-Haematologica-web
P. 113
FLT3-ITD leukemia, DOCK2 and DNA damage response
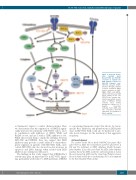
Figure 6. Proposed mecha- nism through which Rac1/DOCK2 and FLT3-ITD cooperate to regulate the DNA damage response in FLT3-ITD leukemic cells. FLT3-ITD activates STAT5, directly or through activation of Rac1. Activated STAT5 leads to activation of CHK1, WEE1, PIM-1 and RAD51, which in turn increases DNA repair activity in the cell. FLT3-ITD also activates mis- match repair activity via acti- vation of ERK1/2. DOCK2
activates Rac1
through its function as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), and also modulates FLT3-ITD expression via regulation of Meis1 and Myb.
activity
as therapeutic targets to combat chemoresistance. Here we demonstrate that the suppression of DOCK2 signifi- cantly increases the sensitivity of FLT3-ITD cells to ara-C in combination with inhibitors of CHK1, WEE1 and RAD51 in vitro, and ara-C with a CHK1 inhibitor in vivo. While these results help to clarify the interplay between FLT3-ITD and DOCK2, they also suggest that DDR inhibitors may provide a useful addition to chemothera- peutic regimens in patients with FLT3-ITD AML, since control FLT3-ITD cells also showed modest increases in apoptosis and DNA damage when treated with DDR inhibitors in combination with ara-C.
The findings in this study suggest that DOCK2/Rac1 activity may play an important role in FLT3-ITD signal- ing, particularly with respect to DDR pathways. DOCK2
is a promising therapeutic target that allows for tissue- specific Rac1 inhibition, and perturbations in DDR path- ways in FLT3-ITD AML could also be harnessed to pro- vide novel strategies for the treatment of this aggressive neoplasm.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank NIH/NCI for grants (R21 CA175667 to ASD, R01 CA090668 and P30 CA006973 to DS and T32 CA60441 to MW), Allegheny Health Network- Johns Hopkins Cancer Research Fund (to ASD), Johns Hopkins Catalyst Award (to ASD), Catherine and Constantinos J. Limas Research Award (to ASD) and the Giant Food Pediatric Cancer Research Fund (to DS) for research funding. DS is also supported by the Kyle Haydock Professorship.
haematologica | 2019; 104(12)
2427