Page 121 - 2019_11 Resto del Mondo-web
P. 121
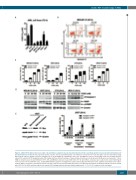
CUDC-907 monotherapy in AML
AB
C
D
E
Figure 1. CUDC-907 treatment decreases viable cells and induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cell lines and shows promise in an acute myeloid leukemia cell line-derived mouse model. (A) Acute myeloid leukemia cell lines were treated with variable concentrations of CUDC-907 for 72 h and viable cells were determined using MTT reagent. Data are shown as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). (B, C) MOLM-13, U937, CTS, and MV4-11 cells were treated with CUDC-907 for 24 h and then subjected to annexin V-FITC/propidium iodine (PI) staining and flow cytometry analyses. Representative dot plots are shown in panel (B). Mean percent annexin V+ cells ± SEM are shown in panel (C). (D) MOLM-13, U937, CTS, and MV4-11 cells were treated with CUDC-907 for 24 h. Whole cell lysates were subjected to western blotting. (E) U937 cells were infected with NTC-, Bax-, or Bak-shRNA lentivirus particles overnight, then washed and incubated for 48 h prior to the addition of puromycin to the culture medium. Whole cell lysates of puromycin-resistant cells were subjected to western blotting (left panel). U937 NTC, Bax knockdown, and Bak knockdown cells were treated with CUDC-907 for 24 h and then subjected to annexin V/PI staining and flow cytometry analysis (right panel). ***P<0.001. (continued on the next page).
haematologica | 2019; 104(11)
2227