Page 69 - 2019_09-HaematologicaMondo-web
P. 69
miR-127 controls HSC maintenance
AB
C
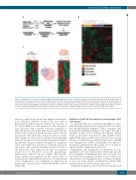
Figure 1. Strategy for the selection of candidate miRNA regulating hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) self-renewal. (A) Experimental workflow. (B) Heat map shows the unsupervised hierarchical clustering of relative miRNA expression in HSC and multi-potent progenitors (MPP) characterized by the absence of the Flk2 marker on their cell surface (Flk2–MPP). The color-scale represents Z-score transformed signal intensity. (C) Hierarchical cluster dendrogram is shown for relative expression of differential expression (DE) miRNA in mutant HSC compared to wild-type (wt) HSC (left) and in the normal HSC-to-MPP transition (right). Venn diagram shows the overlap of deregulated miRNA in the two analyses. The significance of overlap was computed by hypergeometric test (P-value 5x10-5). BM: bone marrow.
However, miR-127-3p showed the highest downregula- tion (>100-fold; miR-99b 3-fold) in the first step of hematopoietic differentiation, whereas the majority of the other miRNA are still expressed at the progenitor level and have only a modest reduction compared to HSC. We then used real-time PCR to investigate whether miR-127-3p is expressed in other hematopoietic cell sub- populations other than HSC within the BM in steady- state conditions. This issue was addressed by analyzing miR-127-3p expression from purified populations includ- ing different lineage committed progenitors, megakary- ocyte and erythrocyte precursors, myeloid precursors and mature cells, and various lymphoid subsets (Table 1 and Figure 2D), since expression in only one subgroup would not be detectable in pooled populations. Impressively, miR-127-3p was highly HSC-specific, being quickly down-regulated in the earliest step of hematopoietic differentiation, where loss of self-renewal occurs. Furthermore, we confirmed its expression in human HSC-enriched CD34+ cells from different sources (Figure 2E).
Inhibition of miR-127-3p function severely impairs HSC self-renewal
To investigate the role of miR-127-3p in HSC we trans- planted lineage-negative (Lin-) cells from CD45.2+ wt mice into lethally irradiated syngeneic CD45.1+ recipients, after permanently inhibiting binding to its targets through a lentiviral sponge vector carrying the reporter protein dGFP, as previously described for other miRNA.11 Since miR-127-3p targets in HSC are not known, we assessed effective downregulation of miR-127-3p activity on K562 cells. Upregulation of XBP-1 and BLIMP-1, two miR-127- 3p targets,21 indicated that the sponge vector worked as expected (Online Supplementary Figure S2).
Engraftment and multipotent reconstitution by Lin- transduced cells was then monitored through periodic blood sampling of transplanted mice and at necropsy sev- eral weeks after transplant. The BM of some of the recon- stituted mice was transplanted into secondary recipients to assess if, in the absence of miR-127-3p activity, HSC maintain their self-renewal ability (Figure 3A).
In primary recipients, survival curves were similar for all
haematologica | 2019; 104(9)
1747