Page 19 - 2019_09-HaematologicaMondo-web
P. 19
Editorials
NHL), including CLL. Compared to other B-NHL, CLL cells have a relatively lower expression of CD20, and sin- gle-agent rituximab has limited activity in CLL. Few stud- ies have investigated the combination of two mAb. The combination of rituximab with the anti-CD52 targeting mAb alemtuzumab yielded a higher rate of complete responses in CLL than had historically been seen with rit- uximab alone.4 However, the manufacturer withdrew alemtuzumab for the treatment of CLL.
Like CD20, the tetraspanin CD37 is an integral mem- brane protein abundantly expressed on B cells but not on plasma cells or hematopoietic stem cells.5 T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, granulocytes, and monocytes express low levels of CD37. Tetraspanins are central to mem- brane organization and play important roles in cell migra-
A
tion and adhesion.6 CD37 has been found to co-localize with integrin a4β1 on B cells and to contribute to cell adhesion and the transduction of survival signals.7
Several anti-CD37 antibodies are undergoing clinical investigation in B-cell malignancies.5 Otlertuzumab (also called TRU-016), a single-chain variable fragment (scFv) against CD37 linked to the IgG1 Fc fragment, induces apoptosis in CLL cells and mediates antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) but not CDC. Otlertuzumab has been shown to have single-agent activ- ity in CLL,8 and in combination with bendamustine increased the response rate and prolonged progression- free survival over single-agent bendamustine.9 BI 836826, a chimeric mouse-human mAb with Fc modifications to increase affinity to FcγRIIIa effectively mediates ADCC
B
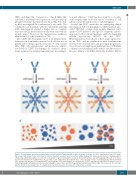
Figure 1. Hexamerization and hetero-hexamerization of CD20- and CD37-targeting mAb on the cell surface. (A) Shown are CD20- targeting (blue) and CD37-target- ing (orange) mAb in IgG1 format. Monomeric in solution, they form hexamers upon cell surface antigen binding. This natural hexamerization of wild-type IgG1 is enhanced by substituting a glutamic acid residue in the IgG1 Fc fragment with a glycine residue (E430G). Mixing CD20- and CD37-targeting mAb leads to the forma- tion of hetero-hexamers in 3:3 (shown here), 4:2, 2:4, 5:1, or 1:5 compositions. (B) Oostindie et al.1 show a gradual increase in complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) mediated by wild-type CD37-targeting IgG1 (left) to wild-type CD20-targeting IgG1 (second from left) to CD37-targeting IgG1 with E430G mutation (center) to CD20-targeting IgG1 with E430G mutation (second from right) to mixed CD20- and CD37-targeting IgG1 with E430G mutation (right). This increase in CDC correlates with the density of C1q docking sites. For simplification, only hetero-hexamers in various 3:3 compositions are shown.
haematologica | 2019; 104(9)
1697