Page 84 - 2019_07 resto del Mondo-web
P. 84
T. Mährle et al.
due to non-specific stimulation, but is antigen-driven and directed against the MDS del(5q) clone. Along this line of reasoning, our findings support the concept that the immunomodulatory effect of lenalidomide not only influ- ences the functional state of T cells, but also induces a pro- found change in the local BM T-cell composition leading to the generation of novel T-cell clusters that can be observed across patients. These clusters, if confirmed by future studies, could also be helpful to explain or even pre- dict resistance or loss of response to lenalidomide.
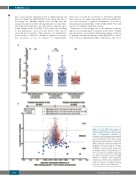
A
Moreover, it would be of interest to determine whether these clusters also appear in patients with non-del(5q) dis- ease and represent a general mechanism of action of lenalidomide independently of the del(5q) MDS. This will need to be addressed in future studies.
Expansion of knowledge about the immune response induced by lenalidomide treatment in the BM of MDS patients may be of particular clinical importance in the era of immune checkpoint therapy. Although MDS is consid- ered to be less immunogenic than solid tumors, the obser-
B
Figure 5. In silico TRB cluster analysis of del(5q) myelodysplastic syndrome bone marrow samples at baseline and after initi- ation of lenalidomide treatment. (A) Frequencies and (B) generation probabilities of in silico-generated TRB clusters in bone marrow mononuclear cells from patients with del(5q) myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) at baseline versus post-lenalidomide treatment. Clusters detected in both were designated as shared and are colored according to their frequency (bright blue decreasing, dark blue increasing on treat- ment). The absolute normalized difference of a cluster was calculated by subtracting the cluster frequencies observed in MDS samples at baseline from frequencies observed in samples after lenalidomide treatment. The size of the dots in (B) repre- sents the numbers of individuals sharing the specific cluster. Lena: lenalidomide.
1362
haematologica | 2019; 104(7)