Page 68 - 2019_07 resto del Mondo-web
P. 68
N. Santana-Codina et al.
a constitutive Ncoa4 KO model,12 in which duodenal Fpn expression was elevated in 2-month old mice but decreased at 6 months.
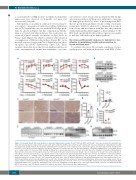
Alternatively, or in addition, serum iron overload may be a secondary consequence of ineffective erythroid utilization of iron. To examine this, we evaluated the Hif-2a-Epo path- way. As shown in Figure 1I,J, this compensatory mecha- nism is activated early after induction. Five weeks later, we observed a trend towards an increase in Epo levels in Ncoa4rec mice (Figure 2G) which correlated with sustained overexpression of Hif-2a in the kidneys (Figure 2H). As in the early response, longer-term Ncoa4 deletion had no effect on spleen size (Online Supplementary Figure S2B). Taken together, these data show that Ncoa4 depletion induces an acute, uncompensated anemia that normalizes over time
and achieves a new steady state in which the Hif-2a-Epo axis response induces erythropoiesis sufficient to overcome the hemoglobin deficit by virtue of producing more RBC that are poorly hemoglobinized. In the setting of adequate serum iron, which is achieved by increased iron export from tissues and iron import from the diet, the persistent cellular hemoglobin deficit suggests a defect intrinsic to the RBC itself, specifically that the erythroid precursor is unable to mobilize sufficient iron for heme synthesis.9
The stress-erythropoietic response to hemolysis is less effective in maintaining erythrocyte production in Ncoa4-deficient mice
To evaluate the role of Ncoa4 under conditions of stress erythropoiesis, we induced hemolysis with PHZ (Online
AB
C
D
F
G
EH
Figure 2. Prolonged Ncoa4 deficiency produces a microcytic hypochromic anemia. Ncoa4fl/fl;UBC-cre/ERT2 and Ncoa4fl/fl mice were treated with tamoxifen and whole blood was analyzed serially and tissue and serum at the endpoint. (A) Whole blood from Ncoa4fl/fl and Ncoa4rec mice was obtained by submandibular bleeding and analyzed at weekly intervals after tamoxifen administration for parameters of the complete blood count [5 mice/group, error bars represent the standard error of mean (s.e.m.)]. (B) Increased Fth1 protein levels in liver and pancreas from Ncoa4rec mice 46 days after initiation of tamoxifen administration. β-actin (Actb) served as a loading control. (C) Increased Fth1 staining in kidney, liver, spleen and pancreas of Ncoa4rec mice 46 days after initiation of tamoxifen administration. Representative field (20x) of 5 mice/group (scale bar = 100 μm) (D) Elevated serum iron levels in Ncoa4rec mice in comparison to Ncoa4fl/fl mice at the endpoint. (3 mice/group, error bars represent the s.e.m.). (E) Fpn protein levels in spleen, liver, and duodenum from Ncoa4rec mice 46 days after initiation of tamoxifen adminis- tration. Actb served as a loading control. (F) Hamp mRNA fold-change in livers of Ncoa4rec and Ncoa4fl/fl mice (n=5/group, error bars represent the s.e.m.). (G) Erythropoietin levels in serum of Ncoa4fl/fl (n=7) versus Ncoa4rec (n=9) mice at day 46 after the initiation of tamoxifen administration (error bars represent the s.e.m.). (H) Increased Hif-2a protein levels in kidneys from Ncoa4rec mice 46 days after the initiation of tamoxifen administration. Actb served as a loading control. For all panels, statistical comparison was performed using a two-tailed Student t-test: *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. RBC: red blood cell count; HCT: hematocrit; HGB: hemoglobin; MCH: mean corpuscular hemoglobin; CHr: reticulocyte hemoglobin content; MCV: mean corpuscular volume; RDW: red blood cell distribution width; RETIC: reticulocyte count; PLT: platelet count; Fth1: ferritin heavy chain 1; Fpn: ferroportin; Epo: erythropoietin.
1346
haematologica | 2019; 104(7)