Page 86 - 2019_01-Haematologica-web
P. 86
A. Guy et al.
P-selectin expression is increased in JAK2V617F endothelial cells
The adhesion of leukocytes to EC is mediated by cell adhesion molecules and selectins.29 Flow cytometry analy- sis demonstrated that JAK2V617F HUVEC expressed intercel- lular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and E-selectin at the same level as JAK2WT HUVEC, whether or not they were previously activated with TNF-α (Figure 4A and Online Supplementary Figure S4). Immunostaining of non-permeabilized carotid arteries from Pdgfb-iCreERT2;JAK2V617F/WT mice showed an increased exposure of P-selectin at the EC surface in vivo, independently of prior administration of TNF-α (Figure 4B,C). Conversely we observed increased levels of soluble P-selectin in the plasma of Pdgfb-iCreERT2;JAK2V617F/WT mice (Online Supplementary Figure S5A). As most soluble P-selectin is of platelet origin, we ruled out an increase of soluble P-selectin due to increased platelet count (Figure 4D). Finally, we excluded increased platelet activation in Pdgfb-iCreERT2;JAK2V617F/WT mice by quantifying soluble platelet factor 4 (Online Supplementary Figure S5B). Collectively, our results support the notion of increased membrane-attached and plasma soluble P-selectin of endothelial origin without an increase in EC expression of ICAM-1, VCAM-1 or E-selectin.
Endothelial expression and release of Von Willebrand factor is increased in JAK2V617F endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo
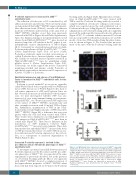
P-selectin is stored within EC in exocytotic organelles called Weibel-Palade bodies together with von Willebrand factor (vWF). Exocytosis of Weibel-Palade bodies leads to cell surface expression of vWF and P-selectin. Since we had observed an increase in endothelial P-selectin expres- sion, we next investigated whether vWF was also increased. In vitro, using immunostaining on non-perme- abilized HUVEC, we observed increased vWF expression at the surface of JAK2V617F HUVEC, spontaneously and after overnight activation with 10 ng/mL TNF-α (Figure 5A). Furthermore, quantification of vWF in the condi- tioned media revealed higher amounts of vWF released by JAK2V617F HUVEC (Figure 5B), a difference that was even greater when the cells had been treated with TNF-α. These results were confirmed in vivo with higher levels of vWF antigen in Pdgfb-iCreERT2;JAK2V617F/WT mice than in control mice (Figure 5C). There was no difference in the distribution of vWF multimers between Pdgfb- iCreERT2;JAK2V617F/WT mice and control animals. These data demonstrate that endothelial JAK2V617F increased the levels of vWF protein and the release of soluble vWF, in associa- tion with increased P-selectin expression at the cell sur- face, as a consequence of increased degranulation of Weibel-Palade bodies.
Increased P-selectin exposure is involved in the pro-adhesive and pro-thrombotic phenotype of JAK2V617F endothelial cells
To investigate a potential causal link between increased P-selectin expression at the EC surface and the pro-adhe- sive phenotype of JAK2V617F EC, we reproduced the same experiments as previously described, but in the presence of a P-selectin blocking antibody. Our in vitro approach with JAK2V617F HUVEC showed a complete reversion of
V617F
the hyper-adhesive properties of JAK2 HUVEC when
these cells had been exposed for 30 min to the P-selectin
blocking antibody (Figure 6A,B). Quantification of leuko- cytes in Pdgfb-iCreERT2;JAK2V617F/WT mice treated with TNF-α and the P-selectin blocking antibody revealed a complete inhibition of leukocyte rolling in control mice, which was expected given the well-established role of P-selectin in leukocyte rolling (Figure 6C). In mutant mice, administration of P-selectin blocking antibody completely reversed the pathologically increased leukocyte adhesion (Figure 6C,D). To examine whether increased P-selectin was also responsible for thrombus formation, we used the model of low-dose TNF-α-induced lung thrombus forma- tion (as shown in Figure 1). We observed that pre-treat- ment of the mice with the P-selectin blocking antibody
A
B
C
Figure 5. von Willebrand factor expression is increased in JAK2V617F-expressing
endothelial cells. (A) Cell surface expression of von Willebrand factor (vWF) (red)
is higher in JAK2V617F human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) (right) than
HUVEC (left). Nuclei are stained by DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 20 mm. (B) JAK2V617F HUVEC secrete more vWF than JAK2WT HUVEC in the absence or pres- ence of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha. Statistical significance was deter- mined by Mann-Whitney test. Results are mean value ± SEM from three experi- ments. (C) Plasma level of vWF antigen (Ag) is increased in Pdgfb- iCreERT2;JAK2V617F/WT mice. Results are expressed as mean value ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by the Student t-test. *P<0.05; ***P<0.001.
in JAK2
WT
76
haematologica | 2019; 104(1)