Page 85 - 2019_01-Haematologica-web
P. 85
JAK2V617F endothelial cells are pro-thrombotic
control, JAK2WT- or JAK2V617F-lentivirus infected HUVEC did not reveal any significant differences in the kinetics or extent of thrombin generation. These results indicate that there is not a significant gain of pro-coagulant activity in response to JAK2WT- or JAK2V617F-induced HUVEC expres- sion (Figure 2A,B). We next hypothesized that JAK2V617F HUVEC might acquire a procoagulant phenotype due to exposure to circulating inflammatory stimuli. We thus repeated the experiments after overnight activation with 10 ng/mL TNF-α, but did not observe any difference (Figure 2A,B). We also measured the rate of thrombin-trig- gered protein C activation and did not observe any differ- ence between the cells (Figure 2C). Finally, we quantified the production of nitrite and prostaglandin (6-keto- prostaglandin 1-α) and did not find any difference between JAK2WT and JAK2V617F HUVEC which were or were not stimulated by TNF-α (Figure 2D,E). To assess whether JAK2V617F EC increase hemostatic potential in vivo, we used whole blood thromboelastometry in Pdgfb-iCreERT2;JAK2V617F/WT mice. No difference was observed in clotting time, clot formation time, 10-minute amplitude or alpha angle after stimulation of the extrinsic pathway (Online Supplementary Figure S3).
JAK2V617F endothelial cells have a pro-adhesive phenotype in vitro and in vivo
Exposing EC to inflammatory stimuli leads to expres- sion of adhesion molecules that allow rolling and adhe- sion of leukocytes, a phenomenon that is thought to par- ticipate in the pathogenesis of thrombosis. Using JAK2V617F- transduced HUVEC, we observed an increase in static adhesion of normal mononuclear cells (Figure 3A) and nor- mal polymorphonuclear neutrophils isolated from healthy subjects (Figure 3B), as previously reported with JAK2V617F EC from patients. Under flow conditions, we also observed that more normal polymorphonuclear neu- trophils rolled and stably adhered to JAK2V617F HUVEC than to JAK2WT HUVEC (Figure 3C-E). To assess whether this pro-adhesive phenotype was also present in vivo, we injected Pdgfb-iCreERT2;JAK2V617F/WT mice with rhodamine to track leukocytes. Using intravital microscopy, we observed mesenteric venules and quantified leukocyte adhesion and rolling. We observed that both leukocyte rolling and adhesion were significantly increased in Pdgfb- iCreERT2;JAK2V617F/WT mice previously exposed to low-dose TNF-α (Figure 3F-H).
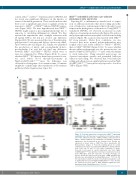
A
BC
D
Figure 4. P-selectin expression is increased in JAK2V617F-expressing endothelial cells. (A) There was no modification of cell surface expres- sion of the adhesion molecules, ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E-selectin on JAK2V617F human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Statistical significance was determined by the Student t-test. Results are expressed as mean value ± SEM from three experiments. (B) Representative images of P-selectin staining (green) in carotid endothelial cells. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue) and VE-cadherin (red). Scale bar: 50 mm. (C) Cell surface expression of mouse P-selectin is increased in carotid endothelial cells from Pdgfb- iCreERT2;JAK2V617F/WT mice whether or not they received tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha. Each dot represents one image (4 images per mouse). Results are expressed as mean value ± SEM. Statistical sig- nificance was determined by the Mann-Whitney test. **P<0.01. (D) The ratio between soluble P-selectin concentration and platelet count is significantly increased in Pdgfb-iCreERT2;JAK2V617F/WT mice. Results are expressed as mean value ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by the Mann-Whitney test. *P<0.05.
haematologica | 2019; 104(1)
75