Page 193 - 2019_01-Haematologica-web
P. 193
CTPA versus V-Q lung scan in pregnant women
absorbed doses than V-Q lung scanning. Importantly, most of the radiation exposures reported in the literature were not measured directly but were calculated and,
therefore, fully dependent on the scan techniques used, which were largely outdated compared to the ones cur- rently used. The higher breast radiation exposure with
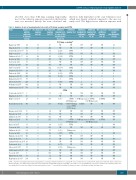
Table 3. Analysis of rate of non-diagnostic test results of V-Q lung scanning and CTPA.
Study Number of Non-diagnostic Non-diagnostic Additional Additional Additional Additional Non-conclusive Anticoagulation
patients subjected to imaging test (n)
Balanetal.1997 82 Chanetal.2002 113 Scarsbook et al. 2007 96 Ridgeetal.2009 25 Shahiretal.2010** 99 Reveletal.2011 91 Scottetal.2011 73
imaging test (n)
33
28 7
17 18.7 1 1.3 22 18.9 13 16.2 5 21.7
imaging test (%)
imaging tests in case of first non-diagnostic test, n (%)
imaging test
imaging test confirming PE (n)
NP
imaging test excluding PE (n)
NP
additional imaging test (n)
despite non-diagnostic results
V-Q lung scanning*
40 NP NP
24,8 NP NP
NP 0 NP
NP 2 NP
NP 12
NP 4 0 0 NP NP
7.3 2 (29) 1 4 1(100) 22 21 3(14)
CTPA
CTPA
CTPA 1 2 0 NP
NP NP NP NP NP NP
NP NP NP NP NP NP 1 9 NA NA
NP NP NP NP NP NP
3 NP NA NA
Sellem et al. 2013
Abele et al. 2013‡
Astani et al. 2014 **
Cuttsetal.2014†
Ramsay et al. 2015†
Richardetal.2015
Sheenetal.2017 225 21 Golfametal.2017 362 29 Armstrong et al. 2017 769 74
Scarsbook et al. 2007 9 1
King-Imetal.2008 40 0 0 NP NP NP
116
74
23
183
127
77 7 9 1
13 (100) CTPA NA NA
6 3.3 2(33) 37 29.1 19 (51)
CTPA 0 0 2 2 CTPA 1 8 10 4 CTPA 0 0 0 2 CTPA 2 5 2 NP
9.3 9(43)
8 NP NP NP
NP NP
NA
NP
NP NP NP NP
NA NP
NP NP 2 (CTPA) NP
NP NP
NP NP NP NP NP NP
2 (CTPA) NP
9.1 NP
11 0(0) NA NA
CTPA
NP NP
Ridge et al. 2009 28 10 35.7 5 (50) 3 CTPA
2 V-Q lung scan 1 (V-Q lung scan)
Bourjeily et al. 2012 343 71 20.7 44 (62) 5 CUS+V-Q lung 1 (CUS) NP scan or CTPA
39 CUS alone
Browneetal.2014 70 1 1.4 NP NP NP NP Moradietal.2015 27 1 3.7 NP NP NP NP
1 (V-Q lung scan) 1 (CTPA)
Shahiretal.2015 95 Ridge et al. 2011 45
11 11.5
10 21.7
NP NP NP NP
5 (50) 3 CTPA 1 (V-Q lung scan) 1 (CTPA)
Bajcetal.2015 61 Scottetal.2011 18 Shahiretal.2010 106 Reveletal.2011 43
Nijkeuter et al. 2013 143 Tomasetal.2013 10 Litmanovitchetal.2009 26 Pottonetal.2009 34 Sheenetal.2017 97
Armstrong et al. 2017 269
Yeoetal.2017 7 4 Mitchelletal.2017 99 12 Halpenny et al. 2017 204 62
2 V-Q lung scan 1(V-Q lung scan)
1(17) CTPA 0 0 1 NP
NP NP NP NP NP NP 3(50) Qlungscan 0 3 0 0
6 9.8
2 11.1
6 5.7
8 18.6 3(37.5) CTPA 0 2 1 NP
8 5.5 NP NP
3 30 NP NP
1 3.8 NP NP
7 20 4(57) NP
9 9.3 3(33) Qlungscan 0 2 1 NP
NP NP NP 1 NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP
23 8.9 NP NP 57.1 NP NP 12 NP NP 30.4 NP NP
NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP NP
CTPA: computed tomography pulmonary angiography; V-Q scanning: ventilation-perfusion scanning; NP: not provided; NA: not applicable. PE: pulmonary embolism; CUR: compression ultrasonography; *non diagnostic V-Q lung scans were defined by intermediate and low probability scan results. †89 low probability V-Q scans were considered as normal V-Q lung scans. ‡non-diagnostic V-Q scans were defined as abnormal perfusion scans. ** very low PE probability V-Q lung scans were considered as normal V-Q lung scans.
haematologica | 2019; 104(1)
183