Page 129 - 2018_11-Haematologica-web
P. 129
Targeting FLT3-ITD in AML
content in MV4-11 cells treated with 20nM PKC412 and 50nM NVP-HDM201 (Figure 4G). Moreover, there was a significant increase in the number of AnnexinV positive apoptotic cells and a concomitant reduction in AnnexinV negative non-apoptotic cells in MV4-11 cells treated with 20nM PKC412 and 50nM NVP-HDM201 (Figure 4H). The pro-apoptotic and lethal effects of the single compound treatments were enhanced in the combined treatments with a combination index of 0.44 indicating synergistic pro-apoptotic and lethal effects with NVP-HDM201 and midostaurin. A similar induction of apoptosis and cell death was also detected in MOLM-13 cells treated with 20nM PKC412 and 50nM NVP-HDM201 (Online Supplementary Figure S2). While there was no pro-apoptot- ic effect in FLT3wt/TP53wt/NPM1mut (OCI-AML3) and FLT3-ITD/TP53mut (PL-21) cells at 100nM compounds, a low-level induction of apoptosis and cell death was detected in OCI-AML3 and PL-21 cells after 24 hours of treatment with 1 mM compounds (data not shown).
In summary, our data indicate that NVP-HDM201 and midostaurin can induce apoptosis and cell death effective- ly and specifically in FLT3-ITD/TP53wt/NPM1wt AML cells. FLT3-ITD is a constitutively active growth factor
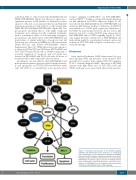
receptor signaling via PI3K-AKT,13 via RAS-MEK-ERK13 and via STAT514,15 leading to cell growth and proliferation via p53 inhibition and MCL1 induction (Figure 5). We have shown that MDM2 inhibition by NVP-HDM201 can reactivate p53 function leading to induction of CDKN1A and inhibition of MCL1 gene expression. Inhibition of FLT3-ITD by midostaurin, however, did not restore p53 function, but led to reduced MCL1 gene expression via RAS-MEK-ERK and/or STAT5 signaling (Figure 5). These data suggest that the combined use of NVP-HDM201 and midostaurin might be a promising treatment option par- ticularly in FLT3-ITD AML relapsed or refractory to con- ventionaltherapy.
Discussion
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) characterized by nor- mal karyotype (NK) and presence of the mutated FLT3 growth factor receptor gene variant FLT3-ITD comprises 27-34% of newly diagnosed AML. The subset of NK-AML patients with high allelic ratio of FLT3-ITD (>0.5) and NPM1 wild type is associated with adverse risk and low-
Figure 5. Schematic representation of the FLT3-ITD signaling pathways and downstream effects. FLT3-ITD is a constitutively active growth factor receptor signaling via PI3K-AKT, via RAS-MEK- ERK and via STAT5 leading to cell growth and proliferation via p53 inhibition and MCL1 induction. p53 function can be reactivated by NVP-HDM201 treatment leading to induction of CDKN1A and inhi- bition of MCL1 gene expression. MCL1 gene expression can be inhibited by NVP-HDM201 via p53 induction and by midostaurin (PKC412) via RAS-MEK-ERK and/or STAT5 signaling.
haematologica | 2018; 103(11)
1869