Page 83 - Haematologica August 2018
P. 83
Haplo versus MSD in AML in CR1
All interactions between donor type and other covariates were tested; a significant interaction according to cytogenetics has been found, thus a stratification (intermediate or high cytogenetics risk AML) with two separate analysis was made.
Propensity score matching was also performed to reduce or eliminate confounding effects. Two MSD were matched with each Haplo using the nearest neighbor or exact matching.28 Matching was done without replacement. Included in the propen- sity score model were: age, year of allo-HSCT, time from diagno- sis to allo-HSCT, conditioning regimen (RIC), source of stem cells, cytogenetics, patient and donor CMV serology status.
All tests were two-sided and P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Analyses were performed using the R sta- tistical software version 3.2.3 (available online at http://www.R- project.org), and propensity score analysis was performed using the ‘MatchIt’.29
Results
Patients, disease and transplant characteristics
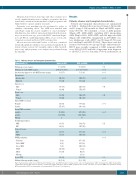
Patients and transplant characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Median follow up was 22 (range 3-96) months and 31 (range 1-116) months for Haplo and MSD, respec- tively (P<0.01). We identified a total of 2654 patients (Haplo=185; MSD=2469), including 2010 intermediate AML (Haplo=1122; MSD=1888) and 644 high risk-AML (Haplo=163; MSD=581) transplanted in 227 EBMT cen- ters. Median age at allo-HSCT was 50 (range 18-74) years for both Haplo and MSD (P=0.63). There were some dif- ferences between the two groups: Haplo underwent allo- HSCT more recently compared to MSD recipients (2014 versus 2010; P<0.01) and had a longer time from diagnosis to allo-HSCT (6 versus 5 months, P<0.01); furthermore, in
Table 1. Patient, disease and transplant characteristics. Characteristic (%)
Median age, years (range)
Median year of allo-HSCT (range)
Interval from diagnosis to allo-HSCT, months (range) Cytogenetics
Intermediate
High risk Patient’s sex
Male
Female
Donor’s sex
Male
Female
Patient CMV serostatus Negative
Positive
Donor CMV serostatus negative
positive
Missing
Conditioning regimen
MAC
RIC
Stem cell source
BM
PBSC
GVHD prophylaxis
CsA alone CsA + MMF Csa + MTX PT-CY Other Missing
In vivo TCD
Median follow-up, months (range)
Haplo (n=185)
50 (18-74)
2014 (2007-2015) 6 (1-17)
122 (66)
63 (34)
103 (56) 82 (44)
96 (52)
89 (48)
28 (15) 155 (85)
51 (28%) 132 (72%) 2
93 (50) 92 (50)
92 (50)
93 (50)
4 (2) 4 (2) 7 (4) 137 (74) 33 (18) 0
54 (31)
22 (3-96)
MSD (n=2469)
50 (18-75)
2010 (2007-2015) 5 (1-18)
1888 (76)
581 (24)
1296 (53) 1172 (47)
1322 (54)
1140 (46)
777 (32) 1660 (68)
927 (38%) 1492 (62%) 50
1302 (53) 1167 (47)
473 (19)
1996 (81)
470 (19) 487 (20) 1273 (51) 36 (2) 182 (7) 21 (1) 863 (35) 31 (1- 116)
P
0.63
<0.01 <0.01
<0.01
0.41
0.43
<0.01
<0.01
0.52
<0.01
<0.01
0.30
<0.01
Haplo: haploidentical family donor; MSD: matched sibling donor; allo-HSCT: allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; CMV: cytomegalovirus; MAC: myeloablative
conditioning regimen; RIC: reduced intensity conditioning regimen; BM: bone marrow; PBSC: peripheral blood stem cells; CSA: cyclosporine; MMF: mycophenolate mofetil; MTX: methotrexate; PT-CY: post-transplant cyclophosphamide; TCD: in vivo T-cell depletion.
haematologica | 2018; 103(8)
1319