Page 43 - Haematologica June
P. 43
JQ1 induces proliferation of HSC
Discussion
Despite the emerging clinical importance of BET inhibitors, a systematic study examining their effects in the adult hematopoietic compartment is urgently needed. We have been able to demonstrate high expression of Brd4 in MK, B cells, T cells and HSC, while it was lower in GMP, monocytes and granulocytes. The expression of Brd2 showed a similar distribution, whereas Brd3 expres- sion was highest in MK and T cells.
In contrast to data with BET inhibitors analyzed in clin- ical studies, JQ1 treatment of mice did not lead to throm- bocytopenia, which might be indicative of species-to- species variations. Interestingly, this comparison is impaired by the fact that JQ1 has never been used in clin- ical studies due to its short half-life in plasma.23 On the other hand, the different effects on thrombopoiesis seen with JQ1 and other BET inhibitors could also be due to minor structural differences between JQ1 and clinical compounds or the drug administration methods.
Further experiments are warranted in order to deter- mine the reasons for the different effects on throm-
bopoiesis exerted by JQ1 in mice and by other BET inhibitors in humans.
In agreement with previous literature, JQ1 treatment led to reduced cellularity in peripheral blood and BM due to reduced numbers of B and T cells.16 We could refine these analyzes showing that JQ1 treatment only led to a reduc- tion of pre-, immature and mature B-cell numbers; howev- er, no decrease in pro-B cells was observed. This might indicate a differentiation block occurring at the pro-B to pre-B transition, which would be in line with the high expression of BET proteins starting at the pro-B-cell level. Despite this hypothesis, we cannot rule out the possibility that JQ1 specifically targets all B-cell subsets except for pro-B cells, thereby reducing their numbers.
Furthermore, JQ1 treatment increased apoptosis in all analyzed T- but not B-cell subsets. We have been able to show that JQ1 decreases mRNA expression levels of the anti-apoptotic BH3 protein BCL2 in the majority of T-cell subsets, whereas no changes in the expression of proapop- totic genes could be detected. However, future studies are needed to understand whether this differential regulation of BCL2 mRNA is directly mediated by the effect of JQ1
ABC
DE
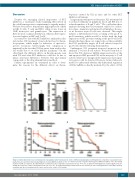
Figure 4. JQ1 treatment increases hematopoietic repopulation after hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) transplantation. Limiting dilution competitive repopulation trans- plantations were performed by transplanting bone marrow (BM) from CD45.1+ JQ1- or control-treated mice together with supporter BM from CD45.2+ mice into lethally irradiated CD45.2+ recipients. (A and B) Analysis of chimerism after competitive repopulation (n=12; *P<0.05). (C) Extreme limiting dilution analysis (ELDA) for deter- mining the frequency of HSC in transplants (n=8-12; *P<0.05). (D and E) Monitoring of chimerism (D) and survival (E) after retransplantation of the BM of primary recipients into the second generation of mice and over the course of 12 months.
haematologica | 2018; 103(6)
945