Page 279 - Haematologica Vol. 107 - September 2022
P. 279
CASE REPORT
A BCDE
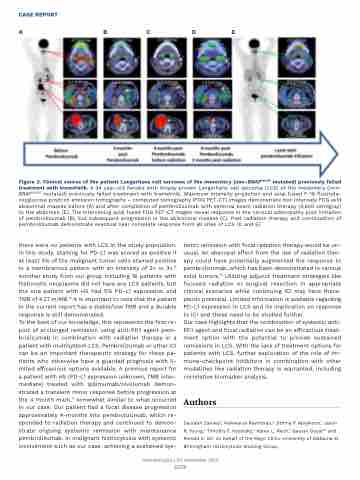
Figure 2. Clinical course of the patient Langerhans cell sarcoma of the mesentery (non-BRAFV600E mutated) previously failed treatment with trametinib. A 34 year-old female with biopsy proven Langerhans cell sarcoma (LCS) of the mesentery (non- BRAFV600E mutated) previously failed treatment with trametinib. Maximum intensity projection and axial fused F-18 fluorode- oxyglucose positron emission tomography – computed tomography (FDG PET-CT) images demonstrate two intensely FDG avid abdominal masses before (A) and after completion of pembrolizumab with external beam radiation therapy (3,600 centigray) to the abdomen (E). The intervening axial fused FDG PET-CT mages reveal response in the cervical adenopathy post initiation of pembrolizumab (B), but subsequent progression in the abdominal masses (C). Post radiation therapy and continuation of pembrolizumab demonstrate eventual near complete response from all sites of LCS (D and E).
there were no patients with LCS in the study population. In this study, staining for PD-L1 was scored as positive if at least 5% of the malignant tumor cells stained positive in a membranous pattern with an intensity of 2+ or 3+.9 Another study from our group including 16 patients with histiocytic neoplasms did not have any LCS patients, but the one patient with HS had 5% PD-L1 expression and TMB of 4.27 m/MB.10 It is important to note that the patient in the current report has a stable/low TMB and a durable response is still demonstrated.
To the best of our knowledge, this represents the first re- port of prolonged remission using anti-PD1 agent pem- brolizumab in combination with radiation therapy in a patient with multisystem LCS. Pembrolizumab or other ICI can be an important therapeutic strategy for these pa- tients who otherwise have a guarded prognosis with li- mited efficacious options available. A previous report for a patient with HS (PD-L1 expression unknown, TMB inter- mediate) treated with ipilimumab/nivolumab demon- strated a transient minor response before progression at the 4 month mark,11 somewhat similar to what occurred in our case. Our patient had a focal disease progression approximately 4-months into pembrolizumab, which re- sponded to radiation therapy and continued to demon- strate ongoing systemic remission with maintenance pembrolizumab. In malignant histiocytosis with systemic involvement such as our case, achieving a sustained sys-
temic remission with focal radiation therapy would be un- usual. An abscopal effect from the use of radiation ther- apy could have potentially augmented the response to pembrolizumab, which has been demonstrated in various solid tumors.12 Utilizing adjunct treatment strategies like focused radiation or surgical resection in appropriate clinical scenarios while continuing ICI may have thera- peutic potential. Limited information is available regarding PD-L1 expression in LCS and its implication on response to ICI and these need to be studied further.
Our case highlights that the combination of systemic anti- PD1 agent and focal radiation can be an efficacious treat- ment option with the potential to provide sustained remissions in LCS. With the lack of treatment options for patients with LCS, further exploration of the role of im- mune-checkpoint inhibitors in combination with other modalities like radiation therapy is warranted, including correlative biomarker analysis.
Authors
Saurabh Zanwar,1 Aishwarya Ravindran,2 Jithma P. Abeykoon,1 Jason R. Young,3 Timothy F. Kozelsky,4 Karen L. Rech,2 Gaurav Goyal1,5 and Ronald S. Go1 on behalf of the Mayo Clinic-University of Alabama at Birmingham Histiocytosis Working Group.
Haematologica | 107 September 2022
2278