Page 151 - Haematologica Vol. 107 - September 2022
P. 151
ARTICLE - FL3B and simultaneous DLBCL
K. Koch et al.
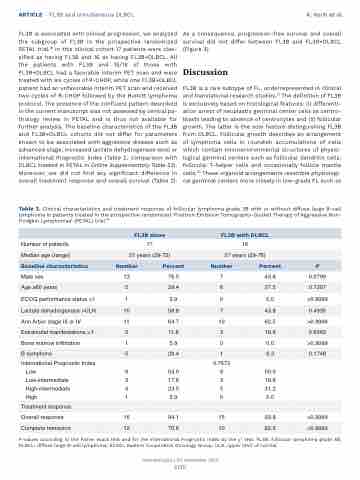
FL3B is associated with clinical progression, we analyzed the subgroup of FL3B in the prospective randomized PETAL trial.18 In this clinical cohort 17 patients were clas- sified as having FL3B and 16 as having FL3B+DLBCL. All the patients with FL3B and 15/16 of those with FL3B+DLBCL had a favorable interim PET scan and were treated with six cycles of R-CHOP, while one FL3B+DLBCL patient had an unfavorable interim PET scan and received two cycles of R-CHOP followed by the Burkitt lymphoma protocol. The presence of the confluent pattern described in the current manuscript was not assessed by central pa- thology review in PETAL and is thus not available for further analysis. The baseline characteristics of the FL3B and FL3B+DLBCL cohorts did not differ for parameters known to be associated with aggressive disease such as advanced stage, increased lactate dehydrogenase level or International Prognostic Index (Table 2, comparison with DLBCL treated in PETAL in Online Supplementary Table S3). Moreover, we did not find any significant difference in overall treatment response and overall survival (Table 2).
As a consequence, progression-free survival and overall survival did not differ between FL3B and FL3B+DLBCL (Figure 3).
Discussion
FL3B is a rare subtype of FL, underrepresented in clinical and translational research studies.21 The definition of FL3B is exclusively based on histological features: (i) differenti- ation arrest of neoplastic germinal center cells as centro- blasts leading to absence of centrocytes and (ii) follicular growth. The latter is the sole feature distinguishing FL3B from DLBCL. Follicular growth describes an arrangement of lymphoma cells in roundish accumulations of cells which contain microenvironmental structures of physio- logical germinal centers such as follicular dendritic cells, follicular T-helper cells and occasionally follicle mantle cells.22 These organoid arrangements resemble physiologi- cal germinal centers more closely in low-grade FL such as
Table 2. Clinical characteristics and treatment response of follicular lymphoma grade 3B with or without diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in patients treated in the prospective randomized ‘Positron Emission Tomography-Guided Therapy of Aggressive Non- Hodgkin Lymphomas’ (PETAL) trial.18
FL3B alone
FL3B with DLBCL
Number of patients
17
16
Median age (range)
51 years (29-72)
57 years (29-76)
Baseline characteristics
Number
Percent
Number
Percent
P
Male sex
13
76.5
7
43.8
0.0799
Age ≥60 years
5
29.4
6
37.5
0.7207
ECOG performance status >1
1
5.9
0
0.0
>0.9999
Lactate dehydrogenase >ULN
10
58.8
7
43.8
0.4935
Ann Arbor stage III or IV
11
64.7
10
62.5
>0.9999
Extranodal manifestations >1
2
11.8
3
18.8
0.6562
Bone marrow infiltration
1
5.9
0
0.0
>0.9999
B symptoms
5
29.4
1
6.3
0.1748
International Prognostic Index
0.7673
Low
9
53.0
8
50.0
Low-intermediate
3
17.6
3
18.8
High-intermediate
4
23.5
5
31.2
High
1
5.9
0
0.0
Treatment response
Overall response
16
94.1
15
93.8
>0.9999
Complete remission
12
70.6
10
62.5
>0.9999
P-values according to the Fisher exact test and for the International Prognostic Index by the c2 test. FL3B: follicular lymphoma grade 3B; DLBCL: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; ECOG:, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; ULN, upper limit of normal.
Haematologica | 107 September 2022
2150