Page 93 - Haematologica May 2022
P. 93
Complement dysregulation & COVID-19
we extend these findings and demonstrate that the SARS- CoV-2 spike protein directly competes with CFH for bind- ing to heparan sulfate. In addition, we demonstrate, for the first time, that COVID-19 patient serum induces com- plement dysregulation on the cell surface using a function- al assay (the mHam). Moreover, a positive mHam is high- ly associated with disease severity in COVID-19 patients, and C5b-9 cell deposition induced by patient sera is blocked by factor D and C5 inhibitors.
Our finding that complement dysregulation is inherent to the pathogenesis of COVID-19 is in agreement with existing preclinical and clinical data. Autopsy studies revealed depositions of complement proteins in lung and other tissues co-localize with the SARS-CoV-2 spike pro- teins.8,24 Markers of complement activation in sera from COVID-19 hospitalized patients are associated with respi- ratory failure. Specifically, markers of classical/lectin (C4d), alternative (C3bBbP) and common pathway (C3bc, sC5b-9) amplification were increased in COVID-19 patient sera throughout hospitalization, indicative of sus- tained activation of all complement pathways.9–11,25 Sinkovits et al.26 showed that complement overactivation and consumption is predictive of in-hospital mortality in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Specifically, these authors reported consumption of C3 in the serum of patients with severe COVID-19 disease. This is consistent with our finding of increased C3c deposition on TF1PIGAnull cells. In tran- scriptome analysis, expression of multiple complement genes such as C2, C3, CFB and CFH were upregulated in COVID-19 patients.27,28 Gavriilaki et al.29 analyzed genetic
Figure 5 (right). SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins compete with complement factor H for the same binding sites on heparin. (A) The binding of complement factor H (CFH) to heparin-linked beads was markedly reduced in the presence of SARS- CoV-2 spike protein subunit 1 (S1) and subunit 2 (S2). The western blot was per- formed using anti-CFH antibody. (B) S1 and S2 retained similarly high binding affinity to heparin-linked beads in the presence and absence of CFH. The west- ern blot was performed using anti-His antibody. The input is the protein solution that is used to incubate with the beads. S: SARS-CoV-2 spike protein; S1: SARS- CoV-2 spike protein subunit 1; S2: SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunit 2.
A
B
C
A
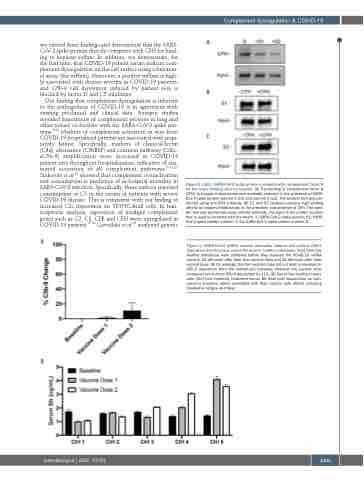
Figure 6. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine minimally induces cell surface C5b-9 deposition but increases serum Bb level in healthy individuals. Sera from five healthy individuals were collected before they received the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine, 24-48 hours after their first vaccine dose and 24-48 hours after their second dose. (A) On average, the first vaccine dose did not lead to elevation in C5b-9 deposition from the individual’s baseline, whereas the second dose increased cell surface C5b-9 deposition by 11%. (B) Two of five healthy individ- uals (Ctrl) had markedly increased serum Bb level post vaccination as com- pared to baseline, which correlated with their vaccine side effects including headache, fatigue and fever.
B
haematologica | 2022; 107(5)
1101