Page 90 - Haematologica May 2022
P. 90
J. Yu et al.
Figure 3. C5b-9 deposition was completely inhibited by blocking the terminal complement pathway with an anti- C5 antibody. The factor D inhibitor (ACH145951), an APC-specific inhibitor, partially reduced C5b-9 deposition induced by serum from patient 2 and achieved complete
inhibition in patient 1 (Figure 3A). In addition, the factor D inhibitor was more effective than anti-C5 antibody in inhibiting C3c deposition triggered by COVID-19 patient sera (Figure 3B), since it targets upstream of the anti-C5 monoclonal antibody.
A
B
C
D
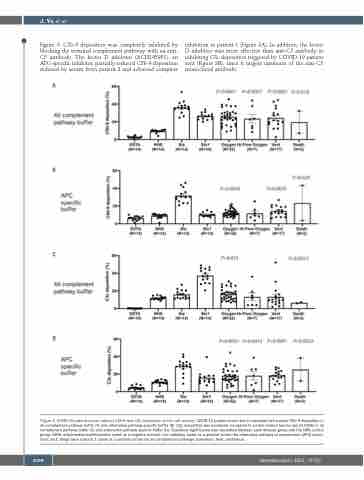
Figure 2. COVID-19 patient serum induces C5b-9 and C3c deposition on the cell surface. COVID-19 patient serum led to increased cell surface C5b-9 deposition in all complement pathway buffer (A) and alternative pathway specific buffer (B). C3c deposition was increased compared to control normal human serum (NHS) in all complement pathway buffer (C) and alternative pathway specific buffer (D). Statistical significance was calculated between each disease group and the NHS control group. EDTA: ethylenediaminetetraacetic (used as a negative control); Sia: sialidase (used as a positive control for alternative pathway of complement [APC] activa- tion); stx1: Shiga toxin subunit 1 (used as a positive control for all complement pathways activation). Vent: ventilation.
1098
haematologica | 2022; 107(5)