Page 150 - Haematologica May 2022
P. 150
A. Dodero et al.
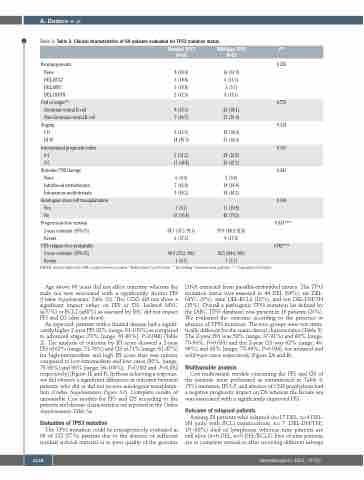
Table 3. Table 3. Clinical characteristics of 69 patients evaluated for TP53 mutation status.
Rearrangements None
DEL-BCL2 DEL-MYC DEL-DH/TH
Cell of origin**
Germinal central B cell Non-Germinal central B cell
Staging I-II
III-IV
International prognostic index
0-2
3-5
Systemic CNS therapy
None
Intrathecal methotrexate Intravenous methotrexate
Autologous stem cell transplantation Yes
No
Progression-free survival
2-year estimate (95% CI)
Events
CNS relapse-free probability
2-year estimate (95% CI)
Events
Mutated TP53 N=16
8 (50.0) 3 (18.8) 3 (18.8) 2 (12.5)
8 (53.3) 7 (46.7)
2 (12.5) 14 (87.5)
5 (31.2) 11 (68.8)
0 (0.0) 7 (43.8) 9 (56.2)
1 (6.2) 15 (93.8)
58.3 (37.3; 91.1) 6 (37.5)
90.0 (73.2; 100)
1 (6.3)
Wild-type TP53 N=53
36 (67.9) 6 (11.3) 3 (5.7) 8 (15.1)
25 (48.1) 27 (51.9)
18 (34.0) 35 (66.0)
28 (52.8) 25 (47.2)
5 (9.4) 14 (26.4) 34 (64.2)
11 (20.8) 42 (79.2)
79.9 (68.9; 92.8) 9 (17.0)
92.5 (84.6; 100)
3 (5.7)
P* 0.258
0.776
0.124 0.161
0.241
0.334 0.033***
0.782***
DH/TH: double/triple hit; CNS: central nervous system. *Fisher Exact test P-value; **Excluding 7 not-assessed patients; ***Log-rank test P-value.
Age above 60 years did not affect outcome whereas the male sex was associated with a significantly shorter PFS (Online Supplementary Table S3). The COO did not show a significant impact either on PFS or OS. Isolated MYC (≥70%) or BCL2 (≥80%) as assessed by IHC did not impact PFS and OS (data not shown).
As expected, patients with a limited disease had a signifi- cantly higher 2-year PFS 92% (range, 81-100%) as compared to advanced stages (70% [range, 61-80%], P=0,048) (Table 2). The analysis of outcome by IPI score showed a 2-year PFS of 62% (range, 51-76%) and OS of 71% (range, 61-85%) for high-intermediate and high IPI score that was inferior compared to low-intermediate and low cases (88%, [range, 79-98%] and 98% [range, 94-100%]; P=0,002 and P=0,002 respectively) (Figure 1E and F). In those achieving a response, we did observe a significant difference in outcome between patients who did or did not receive autologous transplanta- tion (Online Supplementary Figure S1). Complete results of univariable Cox models for PFS and OS according to the patients and disease characteristics are reported in the Online Supplementary Table S4.
Evaluation of TP53 mutation
The TP53 mutation could be retrospectively evaluated in
69 of 122 (57%) patients due to the absence of sufficient residual archival material or to poor quality of the genomic
DNA extracted from paraffin-embedded tissues. The TP53 mutation status was assessed in 44 DEL (64%), six DEL- MYC (9%), nine DEL-BCL2 (13%), and ten DEL-DH/TH (15%). Overall a pathogenic TP53 mutation (as defined by the IARC TP53 database) was present in 16 patients (23%). We evaluated the outcome according to the presence or absence of TP53 mutation. The two groups were not statis- tically different for the main clinical characteristics (Table 3). The 2-year PFS was 58% (range, 37-91%) and 80% (range, 70-93%; P=0.033) and the 2-year OS was 62% (range, 40- 96%) and 88% (range, 78-99%; P=0.036), for mutated and wild-type cases respectively (Figure 2A and B).
Multivariable analysis
Cox multivariate models concerning the PFS and OS of the patients were performed as summarized in Table 4. TP53 mutation, IPI 3-5, and absence of CNS prophylaxis had a negative prognostic impact on OS whereas the female sex was associated with a significantly improved PFS.
Outcome of relapsed patients
Among 28 patients who relapsed (n=17 DEL, n=4 DEL- SH [only with BCL2 translocation], n= 7 DEL-DH/TH), 19 (68%) died of lymphoma whereas nine patients are still alive (n=6 DEL, n=3 DEL/BCL2). Five of nine patients are in complete remission after receiving different salvage
1158
haematologica | 2022; 107(5)