Page 205 - 2022_03-Haematologica-web
P. 205
Letters to the Editor
t(X;6)(p11.1;q23) have been identified.2,10-12 Most of these karyotypes are associated with aggressive AML, requiring intensive treatment.13-15
Interestingly, in rare myeloid leukemia cases, a ‘watch and wait’ policy can be considered, as illustrated by reports of incidental cases with successful ‘watch and wait’ strate- gies (Tables 1,2). These cases include monoclonal infant AML M4/M5-cases with somatic t(8;16); however, t(8;16) can also be present in full-blown AML.10 IMD associated with germline THPO mutations should be seriously consid- ered in families with a positive history of essential throm-
bocytosis and myeloproliferative disease in the elderly (Table 2). Furthermore, we found increasing evidence on somatic T21, GATA1 mutations and del(8)(q23.2q24) in IMD (Table 1,2). SNP array analysis can aid in the identifi- cation of subclonal T21 with small clone sizes. Finally, some aberrations have only been described once, neverthe- less, they might become recurrent, such as a del(5q), SETD2 or germline NSD1 mutation (Tables 1,2).
In conclusion, this review and consensus-based diagnos- tic guideline may aid in clinical decision-making for the rare infant cases with myeloid hyperproliferation (Figure 1),
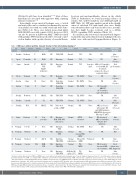
Table 1. IMD-cases without germline (mosaic) trisomy 21 from international database*
UPN Study Age Sex Clinical FAB group presentation1
1 Slovakia Newborn F HSM M7
Genetic tests
Germline
Normal Normal Normal
Normal Normal Normal
Normal Normal Normal
Normal
Somatic
T212 T212 T212
T21, GATA1 T21, GATA1 T21, GATA1
T21, GATA1 T21, GATA1
N/A
SETD2, trisomy 8
T21, GATA1 T21,
(mosaic BM)
GATA1
Mosaic T21,
GATA1
T21, GATA1
Treatment CR/event
N/A CR None CR
Low-dose AML (at 5.5 months); AraC received AML-DS
treatment; progressive disease;
respiratory failure None CR
None CR
None CR (1 month); AML M7
(at 15 months), same aberrations
None CR
None CR
None AML (at 3 years)
2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
10
11 12
13 14
15
FISH, PCR Karyotype N/A Karyotype,
Vital status (FU time)
Alive (6.5 years)
Alive (5 years)
Died
(at 18 months)
Alive
(9 years)
Alive (3 years)
Alive (9.5 years)
Alive (11 years)
Alive (6.5 years)
Alive (3 years)
Alive (3 years)
Alive
Alive (1 year)
Died
(2 days after AML diagnosis)
Japan 1.5months M HSM M7
Japan
Czech Sweden Austria
Slovakia Slovakia Slovakia
Spain
Germany Germany
Germany Germany
Germany
1 month
Newborn 6 days 5 days
Newborn 1 month N/A3
Newborn
6 weeks Newborn
Newborn 3 weeks
Newborn
F
M M F
F F M
M
F M
F N/A
F
HM, CL, VSD Alagille syndrome)
None1 None1 None1
HM, CL CL HM, CL
Few petechiae
None None
ASD II
HSM, VSD
None
FISH
M7 Karyotype, FISH
N/A Karyotype, FISH, PCR
M7 Karyotype, FISH, PCR
N/A FISH, PCR M1 FISH, PCR N/A Not tested
at time of IMD3
M7 Karyotype, FISH, CGH, NGS
(117 genes)
with somatic T21 and GATA1-mutation AML BFM 2004 protocol; CR at day 15; ASCT.
None CR, developed AML (at 4 months),
N/A Karyotype, Normal PCR
N/A Karyotype, Normal PCR
CR after first induction
None CR None CR
Prednison4 CR
None CR (8 weeks), developed AML (at 10 months)
N/A Karyotype, FISH, PCR
N/A Karyotype, FISH, PCR
Normal (fibroblasts)
Normal
N/A Karyotype, 46,XX,idic(21) T21, None CR Alive FISH, PCR (p11)c [15] GATA1 (1 year)
*Inclusion criteria: historical non-TAM, non-JMML cases, cured with no/only symptomatic treatment, age <1 year at diagnosis, diagnosed from 1990-2020. Exclusion criteria: transient abnormal myelopoiesis (TAM) according to WHO definition. 1Questioned for hepatosplenomegaly (HSM), intravascular coagulation, cutaneous lesions (CL), central nervous system (CNS)-involvement or other extramedullary disease.2GATA1 not tested in every case.3IMD diagnosis not definite,was made in retrospect,based on blood counts.4Initial diagnosis acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). AML: acute myeloid leukemia; araC = cytarabine; ASCT: allogenic stem cell transplantation; ASD: atrial septum defect; BM: bone marrow; CGH: compar- ative genomic hybridization; CR: complete remission; DS: Down syndrome F: female; FAB: French-American-British classification; FISH: fluorescence in situ hybridization; FU: follow-up; HM: hepatomegaly; IMD: infantile myeloproliferative disease (unrelated to Down syndrome); M: male; N/A: data not available; NGS: next generation sequencing; PCR: polymerase chain reaction; T21: trisomy 21; UPN: unique patient number; VSD: ventricular septum defect; WHO: World Health Organization.
haematologica | 2022; 107(3)
761