Page 173 - 2022_02-Haematologica-web
P. 173
Ethnic features of DDX41 mutations in ICUS/MDS/AML
A
B
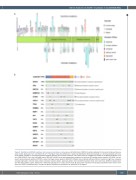
Figure 2. Distribution of DDX41 mutations and concurrent mutations in other genes. (A) Distribution of DDX41 mutations detected in the current study and two pre- vious studies (Quesada et al.10 and Sebert et al.11). This figure shows the differences in positional distribution (N-terminal skewed vs. C-terminal skewed) and muta- tional effects (variable vs. missense-dominated) between germline and somatic mutations. The protein structure of DDX41 was based on the RefSeq accession num- ber of NM_016222.3 and the UniProtKB entry of Q9UJV9: the 622 amino acid long protein comprises the helicase ATP-binding domain (position 212-396), the heli- case C-terminal domain (position 407-567), and a zinc finger domain (position 580-597). Different colors indicate different effects of mutations: light blue, missense mutation; light green, inframe indel; purple, nonsense mutation; brown, splicing mutation; red, frameshift mutation; black, start codon loss. Different shapes repre- sent the three studies: square, Sebert et al.11 diamond, Quesada et al.10 circle, current study. (B) Concurrent mutations of other genes identified in bone marrow sam- ples from DDX41-mutated patients. The types of genetic alterations and diseases are presented in the legend.
haematologica | 2022; 107(2)
515