Page 178 - 2021_12-Haematologica-web
P. 178
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Daratumumab, an original approach for treating multi-refractory autoimmune cytopenia
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) and warm autoim- mune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) are antibody-mediated autoimmune diseases in which plasma cells secrete patho- genic antibodies directed against platelet and red blood cell antigens.1 Some patients show no response to first- or second-line treatments, including corticosteroids, ritux- imab, immunosuppressive drugs, splenectomy and, in the case of ITP, thrombopoietin receptor agonists, a situation
that increases the risk of morbidity and mortality.2,3 In these refractory cases, persistent autoreactive long-lived plasma cells in the bone marrow could explain treatment failure.
Daratumumab, an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody developed to target tumoral plasma cells in multiple myelo- ma,4 was recently found to be effective in antibody-medi- ated diseases, such as autoimmune cytopenia following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation5–11 and systemic lupus.12 Here we report the characteristics and outcome of patients who received daratumumab “off label” (compas- sionate use) for severe refractory ITP or warm AIHA.
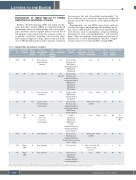
Table 1. Characteristics and outcomes of patients.
Patient Age/ # Sex
1 34/M
2 35/F
3 70/M
4 20/F
5 35/F
6 69/M
Autoimmune cytopenia
ITP
ITP
ITP
ITP
ITP AGS
ITP
Disease duration (months)
95
128
103
174
Active or past underlying disease
Evans syndrome, antiphospholipid syndrome
Evans syndrome
Recurrent venous thrombosis
Ischemic stroke with hemorrhagic transformation
Time from last rituximab infusion
Previous splenectomy
Other previous therapies
Number of Treatments daratumumab given with
infusions daratumumab
Response
Time to Duration of response response (days) (months)
3 Yes
98 No (obesity)
21 Yes
10 Yes
15 Yes
12 No
Relapse
No
Yes
No
NA
Yes
(at 6 months, ITP)
NA
Yes NA
CS (resistant), IVIg (response), HCQ (failure), eltrombopag (failure), MMF (failure), CSA (failure)
CS (resistant), IVIg (response), romiplostim (failure), eltrombopag (failure), MMF (failure), AZA (failure), CSA (failure), CYC (failure)
CS (dependant), MMF (failure), sirolimus (failure), CSA (failure)
CS (resistant), IVIg (response), romiplostim (failure), eltrombopag (failure), MMF (failure), disulone (failure)
For AGS:
CS (failure),
IVIg (failure), MMF (failure). For ITP: romiplostim (failure), eltrombopag (failure), disulone (failure)
CS (response),
IVIg (response), romiplostim (failure), eltrombopag (response then adverse event)
CS (response)
CS (response), AZA (failure), CSA (failure), everolimus (failure), bortezomib (failure)
7 NoneCR712
6 NoneCR353
4 None Failure
NA NA
NA NA
NA NA
NA NA
2 9 NA NA
6 High-dose CS and IVIg
Failure
24 Hodgkin disease (9
6 None Failure
18
74 26
years before daratumumab)
Evans syndrome
Evans syndrome Evans syndrome
4 High-dose CS and IVIg
Failure
7 8
55/F Warm AIHA
55/F Warm AIHA
3 5
No Yes
4 High-dose CS with complete weaning
at 6 weeks 11 None
CR Failure
AGS: acquired Glanzmann syndrome; AIHA: autoimmune hemolytic anemia; AZA: azathioprine; CR: complete response; CS: corticosteroids; CSA: cyclosporine; CYC: cyclophosphamide; DAT: direct antiglobulin test; ITP : immune thrombocytopenia; IVIg: intravenous immunoglobulin; HCQ: hydroxycholoquine; MMF: mycophenolate mofetil; NA : not applicable;
3198
haematologica | 2021; 106(12)