Page 154 - 2021_12-Haematologica-web
P. 154
T. Tang et al.
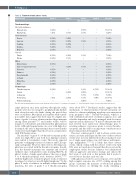
Table 3. Treatment-related adverse events. Adverse event
Non-hematologic
Electrolyte imbalances Hyponatremia Hypokalemia
Gastrointestinal Nausea
Anorexia Vomiting Diarrhea Oralulcer
General Fatigue
Edema Others
Blurred vision
Upper respiratory infection Dysgeusia
Dizziness
Encephalopathy
Lethargy
Rhinorrhea
Rash
Hematologic
Thrombocytopenia Anemia Leukopenia Neutropenia
Febrile neutropenia
Grade 1
3 (27%) 1 (9%)
2 (18%)
3 (27%)
2 (18%)
3 (27%)
2(18%) 0 0
Grade 2
0
1 (9%)
Grade 3 Non-hematologic
8 (73%) 1 (1%)
Grade 4
0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
8 (73%) 0
6 (55%) 7 (64%
0
Any grade
11 (100%) 3 (27%)
7 (64%) 6 (55%) 4 (36%) 4 (36%) 2(18%)
7 (64%) 3 (27%)
4 (36%) 4 (36%) 3(27%) 2 (18%) 2 (18%) 2 (18%) 2(18%) 2 (18%)
11 (100%) 11 (100%) 7 (64%) 11 (100%)
5 (45%)
5 (45%) 2 (18%) 2 (18%) 1 (9%)
0
1 (9%) 0
0
4 (36%) 2 (18%)
4 (36%) 0 3(27%) 2 (18%) 2 (18%) 2 (18%) 2(18%) 2 (18%)
2 (18%) 0
0
1 (9%)
0
2 (18%) 1 (9%)
0
3 (27%) 0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2 (18%) 0
2 (18%)
0
1 (9%) 0
0
1 (9%) 0
0
0
0
0
0
1 (9%) 9 (82%) 1 (9%) 1 (9%) 5 (45%)
The table lists treatment-related adverse events experienced by at least 10% of patients. One patient (9%) developed grade 4 sepsis (not recorded in the table above).
saline infusions and, from mid-way through the study, patients were also encouraged to prophylactically hydrate with electrolyte-rich salt drinks during the period they were on selinexor. Our clinical trial together with current- ly available data suggest that there may be a higher inci- dence of grade 3 or more selinexor-induced hyponatremia among Asian patients16,18-20 and further studies will be required to substantiate and understand this phenomenon better. Although hyponatremia can occur with high-dose ifosfamide, the rates of hyponatremia that occurred in this study were much higher than those based on experiences with ICE therapy alone.
The incidence of grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia in this study was high (82%) and both dose-limiting toxicities were related to low platelet counts. This can be expected given the overlapping toxicities of selinexor and ICE (espe- cially carboplatin). However, there were no bleeding com- plications associated with the thrombocytopenia. In addi- tion, the thrombocytopenia was transient and resolved within 11 days, with platelet counts reaching 75x109/L. In phase I studies of single-agent selinexor, the rates of grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia were between 14-50%,15,16,21 with the higher rates seen in the phase I study of selinexor in relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma.15 In the phase II study of selinexor in multiply relapsed multiple myeloma, the rates of grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia
were about 58%.22 Preclinical studies suggest that the mechanism of selinexor-induced thrombocytopenia are related to selinexor inhibiting megakaryocyte maturation from progenitor cells.23 Thrombocytopenia, which is a well-established side effect of selinexor, appears dose- and schedule-dependent and can be managed with dose inter- ruptions and modifications.24 It may be that patients who had received more myelotoxic chemotherapy, prior to receiving selinexor, were more prone to severe thrombo- cytopenia and this will be an important consideration for future clinical trial development.
The most common grade 1 and 2 adverse events were nausea, anorexia and fatigue and the rates of these adverse events were not very different from those in phase I stud- ies of single-agent selinexor in solid tumors and hemato- logic malignancies.15,16,21 It is likely that these adverse events, which overlap with the adverse events seen with ICE, were not much more frequent than those seen in the single-agent studies because selinexor was administered with an aggressive anti-emetic strategy and only in the first week of each cycle so that patients had 2 weeks to recover before the next cycle was due.
Although not powered to assess response, we found the high complete response rate of 90% striking among this group of patients, the majority of whom had primary refractory disease on entering the study, including a
3174
haematologica | 2021; 106(12)