Page 264 - 2021_06-Haematologica-web
P. 264
Case Reports
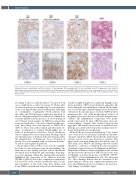
Figure 1. Microscopic investigation of lung tissue. (Line 1) Microscopic investigation of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained lung tissue showed marked vascular congestion, blood extravasation and the presence of microthrombi and megakaryocytes in the interstitial spaces, magnification 20X. (Line 3) Immunohistochemical staining (IHC) revealed positivity for anti-C4d antibody and anti-ICAM-1 antibody, with the presence of inflammatory cells (especially leuko- cytes, both polymorphonucleates and monocytes/macrophages) and the deposition of pro-inflammatory molecules (C1r, C4d) on the endothelial surface , mag- nification 20X.
are similar to those recently described,1-4 because in both cases complications occurred on average 10-15 days after vaccination and were accompanied by a very low platelet count, very high D-dimer and low fibrinogen with signs of consumption coagulopathy.5 Both patients had detectable anti PF-4/polyanion antibodies unrelated to the use of heparin and positive results were confirmed by reactivity inhibition in the presence of excess heparin in vitro.6 Patients tested negative for SARS-Cov-2 molecular assays and antibodies to the nucleocapsid and spike pro- teins, thus ruling out recent exposure to SARS-CoV-2 (Table 1). There was neither clinical and laboratory evi- dence of inherited or acquired thrombophilia nor of intake of prothrombotic medicines. Venous thrombosis was accompanied by severe intracranial bleeding, which was the final cause of death in both and developed after the administration of therapeutic doses of heparin in patient 1 but concomitantly with cerebral vein thrombo- sis and no anticoagulant in patient 2.
The peculiar features of these cases were the availabil- ity of macroscopic and microscopic autopsy findings. The main macroscopic finding was that venous thrombosis was much more widespread and catastrophic than diag- nosed by imaging during life. Immunohistochemistry highlighted the expression of the adhesion molecule VICAM-1 (CD106) and of the complement components C1r and C4d on the vascular endothelial surface in the microcirculation of the heart, lung, liver, kidney and ileum. Diffuse endoluminal and peri-vascular immunore-
activity for IgM and IgG were additional findings in the microcirculation. CD61 revealed platelet aggregates dif- fusely lining the endothelial layer of small- and medium- size vessels and signs of platelet phagocytosis by myeloid elements in the vascular spaces. Scattered CD61-positive immunoreactive cells with morphological features of megakaryocytes were also detected in the lung microvas- culature. The inflammation components were promi- nently represented by large CD163-positive monocyt- ic/macrophagic elements that showed intra-vascular aggregates and variable monocytoid or epithelioid mor- phology, associated with C1r-positive medium-sized ele- ments with granulocyte morphology.
All in all, this post-mortem examination of two typical cases of the novel vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombo- cytopenic syndrome (VITT) shows that the involvement of large venous vessels was much more extensive than appreciated by imaging during the brief clinical course of these fatal cases. Microscopic findings showed vascular thrombotic occlusions occurring in the microcirculation of multiple organs and increased inflammatory infiltrates. Immunohistochemical analyses highlighted the vascular and peri-vascular expression of adhesion molecules such as VICAM1, as well as the presence of CD66b+, CD163+ and CD61+ activated inflammatory cells, also expressing C1r. These findings indicate that the activation of the innate immune system and complement pathway pro- mote the inflammatory process leading to the microvas- cular damage of multiple organs.
2292
haematologica | 2021; 106(8)