Page 232 - 2021_07-Haematologica-web
P. 232
Letters to the Editor
AB
CD
EF
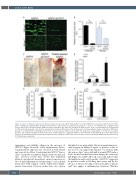
Figure 2. Impact of ACT017 on glycoprotein VI-dependent hemostasis. (A and B) Citrated whole blood from hGPVI mice was labeled with the fluorochrome DiOC6, incubated or not with ACT017 (80 mg/mL) for 10 minutes, and perfused at a wall shear rate of 1,500 s–1 or 100 s–1 for 3 minutes over a collagen-coated surface. Bar=50 mm. (A) Representative images of platelet coverage at the end of the perfusion. (B) Mean surface areas covered by platelets calculated from 20 different fields taken with a 20x objective along channels from four different runs (five fields per run). (C) Representative images of the skin of hGPVI mice treated or not with ACT017 (64 mg/kg) after 4 hours of reverse passive Arthus reaction (rpA). The images are representative of n=4-9 mice per group. Bar=500 mm. (D) Skin hemoglobin content after 4 hours of rpA. # indicates a significant difference (P<0.05) from the rpA hGPVI group, n=6-18 skin biopsies per group. (E and F) Skin myeloperoxidase (E) and platelet factor 4 (PF4) (F) content after 2 hours of rpA, as assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; n=12 skin biopsies per group.
aggregation onto fibrillar collagen in the presence of ACT017 (Figure 2A and B; Online Supplementary Movie), residual platelet adhesion was observed at both arterial and venous blood flow. Considering that ACT017 has no effect on platelet recruitment during cutaneous rpA and that previous results have shown that individual platelets and platelet monolayers ensure hemostasis at sites of mild inflammatory vascular injury,15 such residual interactions with collagen could be sufficient for inflam- matory hemostasis. Previous studies have also shown
that platelets are particularly efficient in maintaining vas- cular integrity in inflamed organs, as platelet counts as low as 10% can support this function.15 Consistent with this notion, Gpvi+/- mice with half of normal GPVI surface levels showed normal hemostasis during the cutaneous rpA (Figure 1C and D). All in all, our results indicate that the highly favorable safety profile of ACT017 suggested by previous results in bleeding time assays and by the absence of adverse bleeding events in the phase I clinical trial12 also applies to inflammatory situations. Whether
2002
haematologica | 2021; 106(7)