Page 22 - 2021_06-Haematologica-web
P. 22
Y. Mathangasinghe et al.
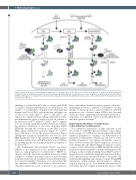
Figure 3. Hsp70 chaperone system modulates the maintenance of dormancy and cell cycle quiescence of stem cell progenitors of erythrocytes. Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) binds and shuttles key cyclins that control proliferation and differentiation of erythroid precursor cells. Growth factor regulated cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKi) appear to modulate these activities by interacting (directly or indirectly) with Hsp70-cyclin complexes. EPO: erythropoietin; HSC: hematopoietic stem cell; SCF: stem cell factor.
shuttling of cyclins A2 and D3 and co-operate with CDKi to regulate terminal differentiation of erythroblasts. An analysis of erythroblasts obtained from differentiating human cord blood CD34+ cells shows that only three out of the seven CDKi (p18INK4c, p19INK4d and p27KIP1) are expressed to significant levels during early and late termi- nal differentiation steps of red blood cells. In contrast to the functions of p57KIP2 and p27KIP1 in HSC, p19INK4d appears to be promoting erythroblast differentiation by facilitat- ing nuclear localization of the stress inducible Hsp70 (HSPA1A) through the activation of the ERK, but not AKT, signal transduction pathway (Figure 3).47 p19INK4d may even play a role in the proteostasis-based fitness checkpoints in human erythroblasts (see below). How EPO stimulation leads to the induction and ERK-mediat- ed nuclear translocation of Hsp70 and the role of CDKi in modulating this process during erythropoiesis remains to be dissected.53,54
The mammalian mitochondrial Hsp70 (mortalin/ HSPA9) is also implicated in the proliferation/mainte- nance of early progenitors of erythrocytes.55 HSPA9 co- operates with the inner mitochondrial translocase (TIM) complex to facilitate the translocation of mitochondrial matrix proteins that are essential for mitochondrial func- tion and cell viability.56 Therefore, it is conceivable that any depletion of HSPA9 levels leads to increased mito- chondrial dysfunction and activation of pro-apoptotic
factors that induce hematopoietic progenitor cell death.57 Intriguingly, however, compared to progenitors of other lineages of hematopoiesis, a greater reduction of BFU-E progenitors was observed when HSPA9 was knocked down in rodents, suggesting that this Hsp70 paralog pos- sibly plays an additional role(s) in maintaining the ery- throid progenitor cell niche.58
Hsp70 checks the fitness of erythroblasts at the initiation of erythropoiesis
The continuous generation of large amounts of red blood cells to traffic O2/CO2 in vertebrates comes with a heavy energy cost (ATP-wise). By allowing only healthy erythroid progenitors to undergo cell differentiation in part increases the fidelity of this process. In order to select healthy progenitors, two fitness checkpoints seem to have evolved around the Hsp70 chaperone system. In both checkpoints, the Hsp70 chaperone appears to mon- itor proteostasis deficiencies in EPO stimulated erythroid progenitors that are primed to undergo differentiation. By acting as a sensor of global folding status, Hsp70 is able to gauge the levels of misfolded/aggregated proteins in these cells. The first fitness checkpoint seems to be initiated by momentarily triggering a pro-apoptotic insult during EPO stimulation, which induces mitochondria to undergo transient depolarization.59 This prompts the activation of several pro-apoptotic signals including the release of the
1524
haematologica | 2021; 106(6)