Page 54 - 2021_05-Haematologica-web
P. 54
X. Li et al.
E
F
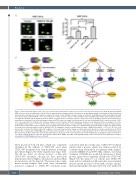
Figure 6. CUDC-907 downregulates c-Myc expression enhancing the antileukemic activity of venetoclax in acute myeloid leukemia cells. (A) Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells were treated, as indicated, for 16 or 24 hours and western blot analysis of whole cell lysates are shown together with the fold changes for the densitometry measurements, normalized to β-actin and then compared to vehicle control. (B) AML cells were treated as in panel A. Total RNA was isolated and c-Myc transcripts were measured by real-time RT-PCR. **P<0.001 compared to control. (C) U937 cells were infected with Precision LentiORF c-Myc or RFP control lentivirus particles overnight, then washed and incubated for 24 hours. Whole cell lysates from one aliquot of cells were subjected to western blotting (top panel). Densitometry meas- urements were normalized to b-actin; fold changes compared to RFP control are shown. The other aliquot of cells were treated with vehicle control, venetoclax, CUDC- 907, or in combination for 24 hours. Flow cytometry analysis results of Annexin V-FITC/PI staining are shown as mean Annexin V positive ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (bottom panel). ***P<0.001. (D) U937 cells were treated with vehicle control, 10058-F4, venetoclax, or in combination for 24 hours. Representative western blots of c-Myc and b-actin are shown (top panel). Densitometry measurements of c-Myc were normalized to β-actin; fold changes compared to vehicle control are shown. Flow cytometry analysis results of Annexin V-FITC/PI staining are shown as mean Annexin V positive ± SEM (bottom panel). ***P<0.001. (E) U937 cells were treated as in panel D and then subjected to alkaline comet assay. Representative images are shown (left panel). Results are shown as median percent DNA in tail from three replicate gels ± SEM (right panel). (F) Proposed mechanisms of action of venetoclax in combination with CUDC-907. CUDC-907 treatment increases Bim and decreases Mcl-1, but Bcl-2 sequesters Bim, which opposes apoptosis. Venetoclax treatment reduces Bim binding to Bcl-2, tipping the balance towards more “free” Bim, inducing apoptosis. CUDC-907 downregulates CHK1, Wee1, RRM1, and c-Myc, inducing DNA damage, while venetoclax prevents DNA repair, leading to accumulation of DNA damage and more cell death.
Mcl-1 protein in both cell lines, which was completely abolished by the addition of CUDC-907, even when CUDC-907 treatment alone only moderately downregu- lated Mcl-1 (Figures 3B; Online Supplementary Figure S3B). We did not detect an obvious increase of Bim after CUDC-907 treatment, though we have previously demonstrated that at higher concentrations increased Bim protein levels could be detected.11 However, in the combi- nation treated samples, Bim levels were substantially increased compared to CUDC-907 treatment alone.
Consistent with the cell line data, CUDC-907 treatment reduced Mcl-1 protein, which was further reduced by combined drug treatment in four primary AML samples. As in the MOLM-13 and U937 AML cell lines, venetoclax treatment of AML#1 also resulted in an increase of Mcl-1 protein, again it was completely abolished by CUDC-907 (Figure 3C). In contrast to our cell line data, CUDC-907 alone and its combination with venetoclax caused marked increase in Bim protein. For both AML cell lines and pri- mary patient samples, Bcl-2 protein levels were unaffected
1274
haematologica | 2021; 106(5)