Page 304 - 2021_04-Haematologica-web
P. 304
Case Reports
Biallelic IARS2 mutations presenting as sideroblastic anemia
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (ARS) are evolutionarily conserved enzymes that catalyze amino acid attachment to their cognate transfer RNA (tRNA), ensuring accuracy of the translation process. Two separate sets of cellular ARS are required, as translation takes place in two dis- tinct compartments, namely cytosol and mitochondria. Eighteen ARS act exclusively in the cytosol (ARS1), 17 act exclusively in the mitochondria (ARS2) and two ARS are bifunctional, as they act in both compartments.1 Mutations in the nuclear genes encoding ARS2 have emerged as a new group of mitochondrial diseases, inconsistently impairing oxidative phosphorylation.2 Among them, pathogenic variants in the IARS2 gene (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man [OMIM] 612801) have been reported to cause overlapping clinical pheno- types ranging from isolated cataract to a syndromic con- dition with cataract (CA), growth hormone deficiency (G), sensory neuropathy (S), sensorineural hearing loss (S), and skeletal dysplasia syndrome (CAGSSS) OMIM 616007) and Leigh syndrome (Table).3-8
Here, we report on biallelic pathogenic IARS2 variants in three unrelated siblings presenting with neonatal sider- oblastic anemia mimicking Pearson syndrome.
Patient 1, the third child of non-consanguineous healthy parents of French origin, was born after a normal full-term pregnancy with normal birth parameters. His older sister and brother are healthy (Figure 2). At birth, he presented with severe sideroblastic anemia (hemoglobin 5.1 g/dL, normal>14.5 g/dL) with normal mean corpuscu- lar volume (MCV). Myelogram showed 2% of ring sider-
oblasts (Figure 1D). Search for B19 parvovirus, Coombs test and Kleinhauer test were negative. Plasma B12 and folate were normal. He required two red blood cell trans- fusions during the first month and thrombopenia reached a nadir of 80.000 platelets/mm3 normal >150.000 platelets/mm3). Plasma lactate (3.8-5.3 mmol/L, normal <2 mmol/L), lactate/pyruvate ratios (33, normal <20) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) lactate were elevated (3.9 mmol/L, normal <2 mmol/L). The child had exocrine pancreatic dysfunction with decreased fecal elastase (75 mg/g, normal 200-500 mg/g) and hypoparathyroidism (plasma calcium 1.24 mmol/L, normal 2.2-2.7 mmol/L; plasma phosphate 2.8 mmol/L, normal 1.12-1.45 mmol/L; parathormone 3 pg/mL, normal: 10-55 pg/mL). He presented with congenital bilateral cataract, axial hypotonia, peripheral dystonia and motor delay. At 6 months, he developed pharmaco-resistant infantile spasms with hypsarrhythmia on electroencephalogram (EEG) and vigabatrin and topiramate were started. Metabolic work-up, including plasma amino acids and liver enzymes (aspartate amino transferase/alanine amino transferase [ASAT/ALAT]), urinary organic acids and skeletal X-ray were normal. Brain magnetic reso- nance imaging (MRI) (3 months) was normal except for a lactate peak on spectroscopy (Figure 1A). The child died at 16 months due to respiratory distress in a context of inhalation pneumonia.
A next-generation sequencing panel targeting genes involved in mitochondrial disorders showed two com- pound heterozygous IARS2 variants: a novel nonsense variant inherited from his father (c.891G>A; p. Trp297*), predicted to result in either nonsense-mediated (NMD) or loss of the terminal two thirds of the protein including
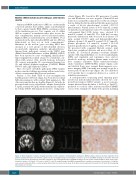
Figure 1. Brain magnetic resonance imaging anomalies in three patients carrying biallelic pathogenic IARS2 variants and bone marrow aspiration from patients 1 and 2. (A) Patient 1 (3 months): sagittal T1, axial T2 weighted images and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) showing no anomalies other than a lactate peak (arrow). (B) Patient 2 (2 months): sagittal T1, axial T2 weighted images and MRS showing no lactate peak but mild and diffuse white matter hyper- intensities (arrows). (C) Patient 3 (7 years): coronal T2, axial T2 weighted images and MRS showing bilateral cavitations in putamen characteristic of Leigh dis- ease (arrows), frank and diffuse cerebral atrophy, white matter loss and a lactate peak. (D, E) Bone marrow aspiration from patient 1 (D) and 2 (E) showing ring sideroblasts on iron stain.
1220
haematologica | 2021; 106(4)